Ymx+c Explained

Linear Relations And Their Graphing Step By Step Math Problem Solver
Linear Graphs Y Mx C Gcse Physics Youtube
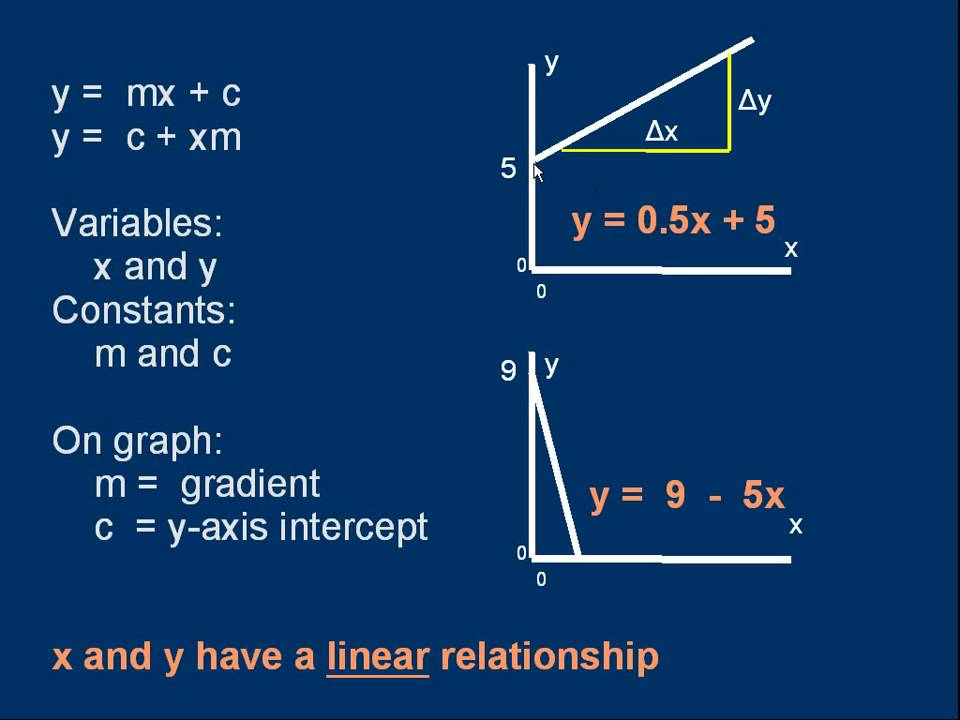
Gce A Level Physics G5 Data Analysis Using Y Mx C Youtube
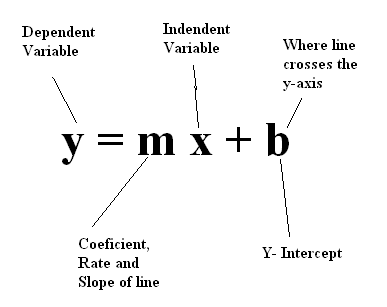
Y Mx B Lessons Blendspace
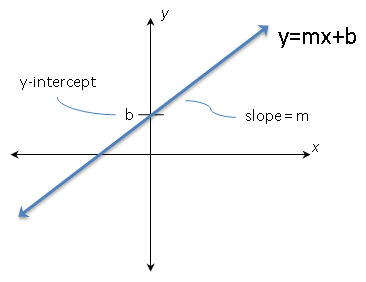
Chapter 4
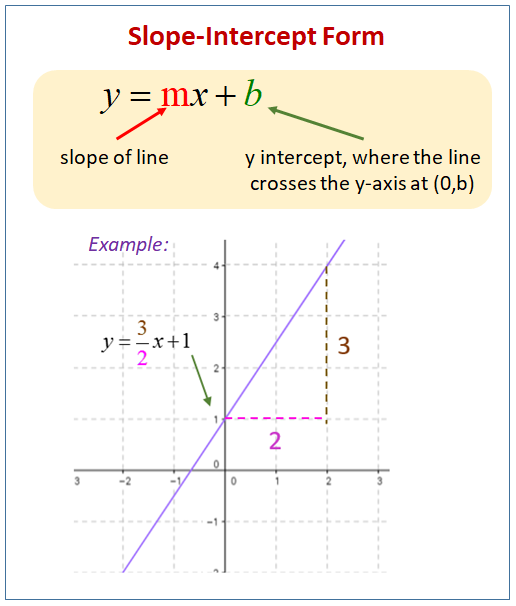
Equation Of Line Solutions Examples Videos
And that the line has an yintercept of (0, 1) which could have been determined from the cvalue which is 1 If you have an absolute value of a that is greater than 1 the parabola will be narrower than the parental quadratic function And the opposite that if you have a absolute value of a that is less than 1 then the parabola will be wider.
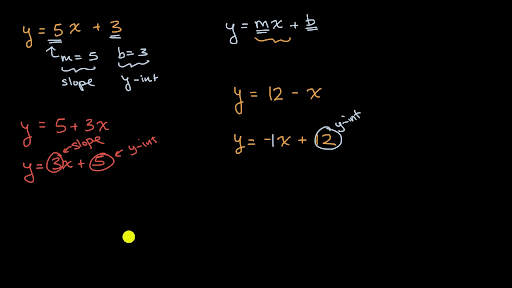
Ymx+c explained. The formula for a line is Y = mxb Y is the output or the prediction M is the slope or the “weight” given to the variable X X is the input you provide based on what you know b is the intercept Essentially given 0 for your input, how much of Y do we start off with Technically regression “minimizes the sum of the square of the error”. For the sake of backpropagation, I assume you are familiar with Gradient Descent which will be explained better in a lot of other places Let’s say you train the model 100 times on the y=mx c. Y = mx c We are now going to use a straight line in order to see how the equation above can be determine and how the xcoordinate or the ycoordinate could be determined if one of the two and the equation is available Fig 1 Fig 1 above shows a straight line graph The gradient of the graph can be determined using the method described here.
Every straight line can be represented by an equation y = mx b The coordinates of every point on the line will solve the equation if you substitute them in the equation for x and y The slope m of this line its steepness, or slant can be calculated like this. #plot a horizontal line along mean of y line2 = npfull(mx,m_y) pltscatter(x,y) pltplot(x,line2, c = 'r') pltshow() The output is given below in fig5 Write the below given code and. Y = mx c represents a straight line graph At any place on the horizontal (or "x") axis the line passes through a particular place on the other (vertical, or "y") axis, where the two axes are.
Slopeintercept form, y=mxb, of linear equations, emphasizes the slope and the yintercept of the line Watch this video to learn more about it and see some examples Slopeintercept form, y=mxb, of linear equations, emphasizes the slope and the yintercept of the line Watch this video to learn more about it and see some examples. 1,2,3,4,5 What we’re going to do is play around with these numbers and see what happens?. The equation of a straight line In this video, I'll show you how to draw the line and the equation associated with y= mxc I'll help you to understand ea.
Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep. Equation of a Straight Line The equation of a straight line is usually written this way y = mx b (or "y = mx c" in the UK see below). The voltage read by arduino is first converted into resistance using equation of straight line ie Y = mX C Here we have to calculate the value of m (slope) and C (constant) For slope we have to measure voltage and resistance at two different temperature let say at 30 0 C and 150 0 C At temperature T 1 (30 0 C) V T1 = 009V.
If y=mxc where m and c are arbitrary constants then differential equation corresponding to given family of lines will be Option 1) Option 2) Option 3) Option 4) Post Answer Answers (1) H Himanshu As we learnt Formation of Differential Equations Let y and x be the dependent and the independent variables respectively. Const It is an optional argument that specifies whether the constant value c to equal 0 If const is TRUE or omitted, c is calculated normally If const is TRUE or omitted, c is calculated normally If false, c is taken as 0 (zero), and the values of m are adjusted so that y = mx. In the equation of a straight line (when the equation is written as "y = mx b "), the slope is the number "m" that is multiplied on the x, and "b" is the yintercept (that is, the point where the line crosses the vertical yaxis) This useful form of the line equation is sensibly named the "slopeintercept form".
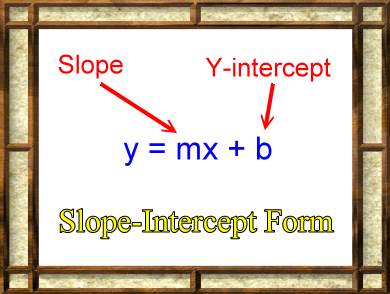
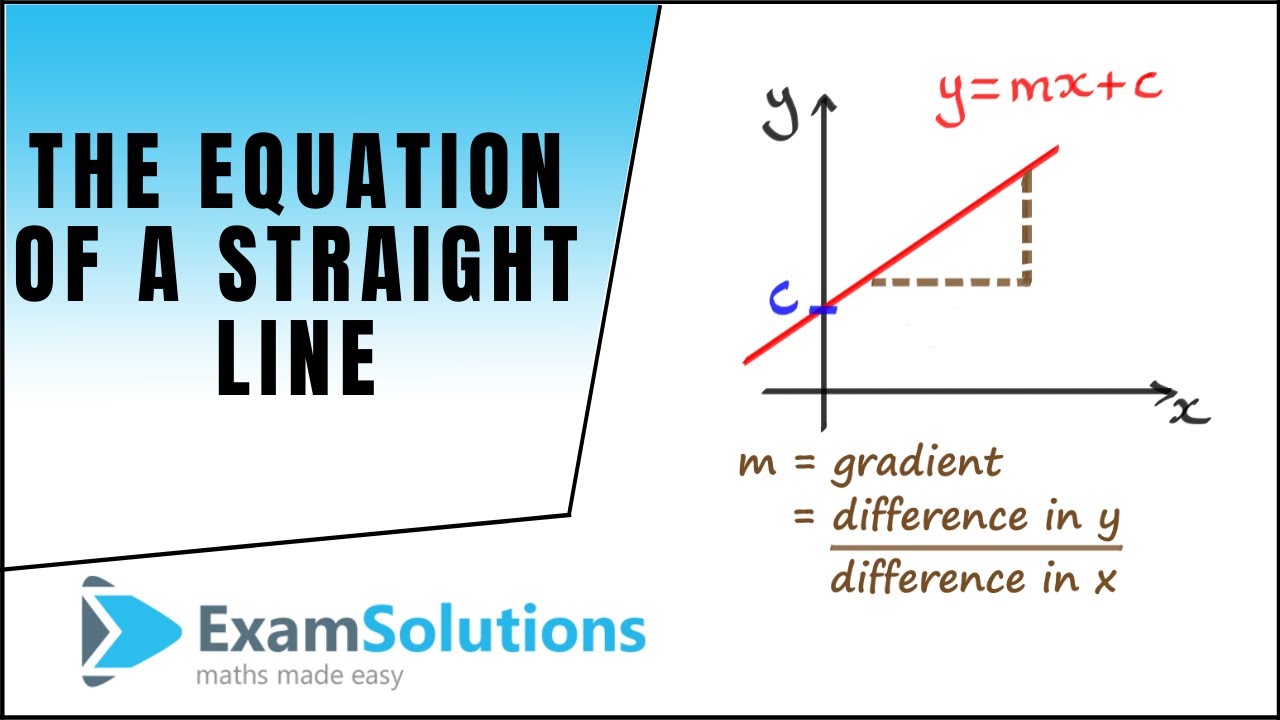
Such an equation is usually written y=mxb ("y=mxc" in the UK) "y=mxb" is the formula of a straight line drawn on Cartesian coordinate system in which "y" is the vertical axis and "x" the horizontal axis In this formula y tells us how far up the line goes. The general equation of a straight line is y = mxc, where m is the gradient, and y = c is the value where the line cuts the yaxis This number c is called the intercepton the yaxis Key Point The equation of a straight line with gradient m and intercept c on the yaxis is y = mxc wwwmathcentreacuk 5 c mathcentre 09. Yeah, what they all said!.
Equation of a Straight Line Equations of straight lines are in the form y = mx c (m and c are numbers) m is the gradient of the line and c is the yintercept (where the graph crosses the yaxis) NB1 If you are given the equation of a straightline and there is a number before the 'y', divide everything by this number to get y by itself, so that you can see what m and c are. Let's multiply them all by. SlopeIntercept Form of a Line (y = mx b) The slopeintercept is the most “popular” form of a straight line Many students find this useful because of its simplicity One can easily describe the characteristics of the straight line even without seeing its graph because the slope and yintercept can easily be identified or read off from.
Straight line equation y=mxc Straight line equation y=mxc Log InorSign Up Move the sliders for 'm' and 'c' to change the gradient and yintercept of this line 1 y = mx c 2 c = 3 3 m = 0 9 4 Here is the graph of the perpendicular to the original line Make it visible by clicking the circle. Y = mxc where m and c are fixed numbers, (ie constants), has a graph which is a straight line For example, y = 3x5, y = 2 3 x8 and y = −3x− 7 all have graphs which are straight lines Theslopeandinterceptofastraightline In the equation y = mxc the value of m is called the slope, (or gradient), of the line It can be positive, negative or zero. For the sake of backpropagation, I assume you are familiar with Gradient Descent which will be explained better in a lot of other places Let’s say you train the model 100 times on the y=mx c.
The voltage read by arduino is first converted into resistance using equation of straight line ie Y = mX C Here we have to calculate the value of m (slope) and C (constant) For slope we have to measure voltage and resistance at two different temperature let say at 30 0 C and 150 0 C At temperature T 1 (30 0 C) V T1 = 009V. C) We write 4x−y 13 = 0 in standard form as y = 4x13 and note that m = 4, c = 13 d) Comparing y = 8 with y = mxc we see that m = 0 and c = 8 This line is horizontal e) Comparing y = 4x with y = mxc we see that m = 4 and c = 0 Exercises 1 State the gradient and intercept of each of the following lines. Y = mx c Linear regression is nothing but a manifestation of this simple equation y is the dependent variable ie the variable that needs to be estimated and predicted x is the independent variable ie the variable that is controllable It is the input m is the slope It determines what will be the angle of the line.
Find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to Y=2X4 at (2,8) I'm really stuck with how you work this out and any help would be appreciated, please include the steps taken to find the answer!. Probability concepts explained Maximum likelihood estimation For a linear model we can write this as y = mx c In this example x could represent the advertising spend and y might be the revenue generated m and c are parameters for this model Different values for these parameters will give different lines (see figure below). Arrow_back Back to Working with y = mx c Working with y = mx c Worksheets with Answers Whether you want a homework, some cover work, or a lovely bit of extra practise, this is the place for you And best of all they all (well, most!) come with answers Contents Mathster;.
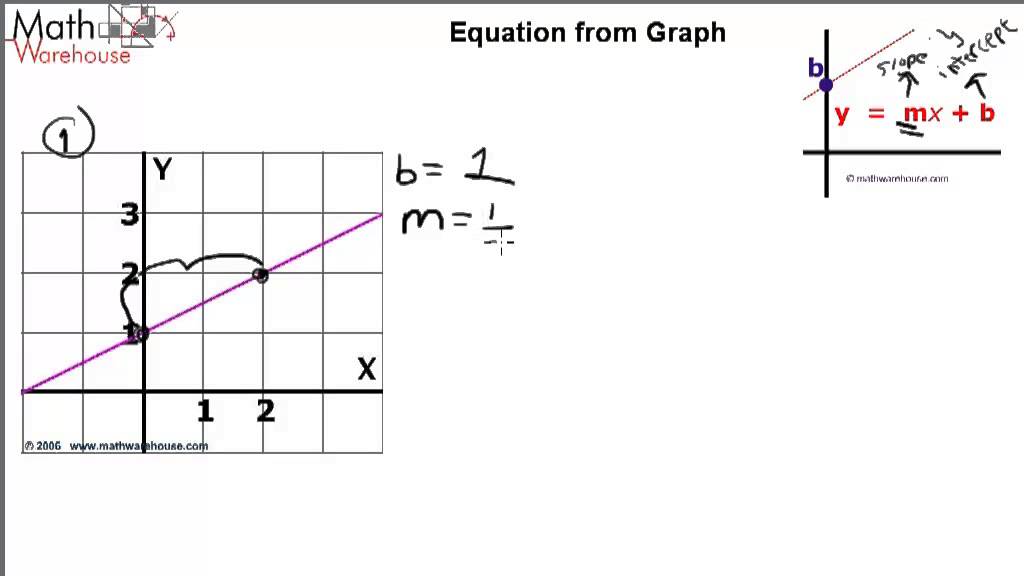
Beer’s Law, A=Ebc, helped to develop the linear equation, since absorbance was equal to y, Eb was equal to m, and the concentration, c, was equal to the slope, x, in the equation y=mxb To calibrate the spectrometer, a solution containing 500 mL of water, 100 mL of ammonium molybdate reagent, and 04 mL of aminonapthosulfonic acid was used. Equations of straight lines are in the form y = mx c (m and c are numbers) m is the gradient of the line and c is the yintercept (where the graph crosses the yaxis) NB1 If you are given the equation of a straightline and there is a number before the 'y', divide everything by this number to get y by itself, so that you can see what m and. Y = mx c, where m is the gradient and c is the yintercept Example Find the equation of the line with gradient 3 and yintercept 4 Here m = 3 and c = 4 We substitute the values of m and c into the equation to obtain y = 3x 4 Exercise Find the equations of the straight lines with the following gradients and yintercepts 1.
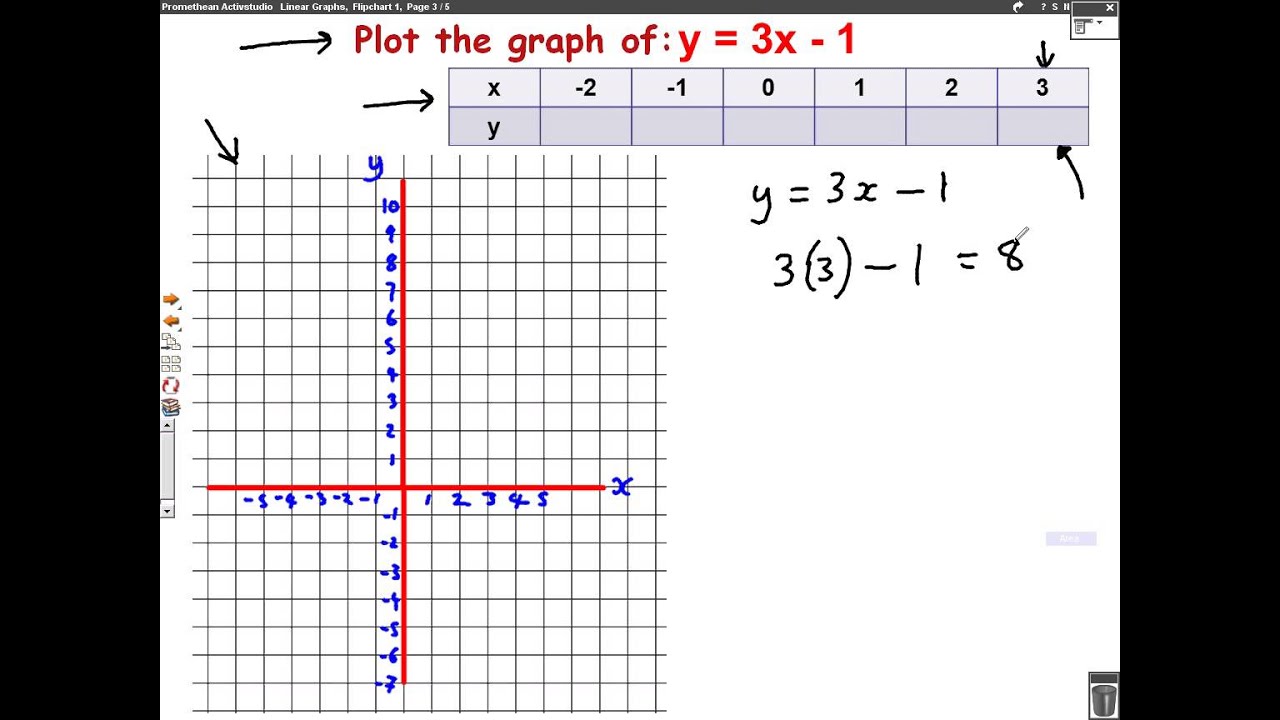
Functions of the form \(y=mxc\) are called straight line functions In the equation, \(y=mxc\), \(m\) and \(c\) are constants and have different effects on the graph of the function Worked example 1 Plotting a straight line graph. Solve for x y=mxb Rewrite the equation as Subtract from both sides of the equation Divide each term by and simplify Tap for more steps Divide each term in by Cancel the common factor of Tap for more steps Cancel the common factor Divide by Move the negative in front of the fraction. Beer’s Law, A=Ebc, helped to develop the linear equation, since absorbance was equal to y, Eb was equal to m, and the concentration, c, was equal to the slope, x, in the equation y=mxb To calibrate the spectrometer, a solution containing 500 mL of water, 100 mL of ammonium molybdate reagent, and 04 mL of aminonapthosulfonic acid was used.
And written in more standard y = mx b notation, y = 2x 2 Let's double check We start at (0, 2) and go 3 units on the x coordinate Our final position is 2*3 2 = 6 2 = 4, which matches up with (3, 4) This approach is slower than a plugandchug shortcut, but the idea is to figure out exactly what you're doing. Instructor What I'd like to do in this video is a few more examples recognizing the slope and yintercept given an equation So, let's start with something that we might already recognize. Y = mx c is an important reallife equation The gradient, m, represents rate of change (eg, cost per concert ticket) and the yintercept, c, represents a starting value (eg, an admin fee).
Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep. Y = mx c, where m is the gradient and c is the yintercept Example Find the equation of the line with gradient 3 and yintercept 4 Here m = 3 and c = 4 We substitute the values of m and c into the equation to obtain y = 3x 4 Exercise Find the equations of the straight lines with the following gradients and yintercepts 1. This is a linear function showing a relationship between x and y For y = mx c, we have y expressed as a function of x, whereby any increase in x is calculated to be an (m times x) increase in y The c value is the value of y when x = 0 If this function is graphed as a line, m is the slope of that line and c is the yintercept.
This yields a model described by the equation y = mx y 0, where y is the instrument response, m represents the sensitivity, and y 0 is a constant that describes the background The analyte concentration (x) of unknown samples may be calculated from this equation. I feel that having something basic like this that directly answers how to plot y=mx c might be useful to others in future though In this case, plotting the axis with geom_hline() and geom_vline() would have been enough to demonstrate that the graph was in fact correct, and that I am in fact too tired – baxx Nov 11 '18 at 1442. I've been trying to teach this stuff for years Can I add some thoughts?.
Key Question 2 C is the mid point of AB and CD is perpendicular to AB Find the equation of CD mAB = 10 – 5 mCD = 3 /5 (m1m2 = 1) C = (3½ , 7½) (mid pt) m = 3 /5 , (a , b) = (3½ , 7½) y – b = m(x – a) y – 7½ = 3 /5(x – 3½) 5y – 37½ = 3(x – 3½) 5y – 37½ = 3x 10½ 5 – 2 = 5 /3 A (2 , 5) B(5 , 10) D C (3½ , 7½. C=ymx Subtract mx from both sides mxc=y Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side mx=yc Subtract c from both sides xm=yc The equation is in standard form \frac{xm}{x}=\frac{yc}{x} Divide both sides by x m=\frac{yc}{x} Dividing by x undoes the multiplication by x. Let's take the first 5 numbers;.
Y = mx c We are now going to use a straight line in order to see how the equation above can be determine and how the xcoordinate or the ycoordinate could be determined if one of the two and the equation is available Fig 1 Fig 1 above shows a straight line graph The gradient of the graph can be determined using the method described here. Y=MXC help (Maths) with explanation?. HSFIFC7, HSFIFC7a, HSFLE Learn about the slopeintercept form of twovariable linear equations, and how to interpret it to find the slope and yintercept of their line Google Classroom Facebook Twitter Email Intro to slopeintercept form Intro to slopeintercept form.
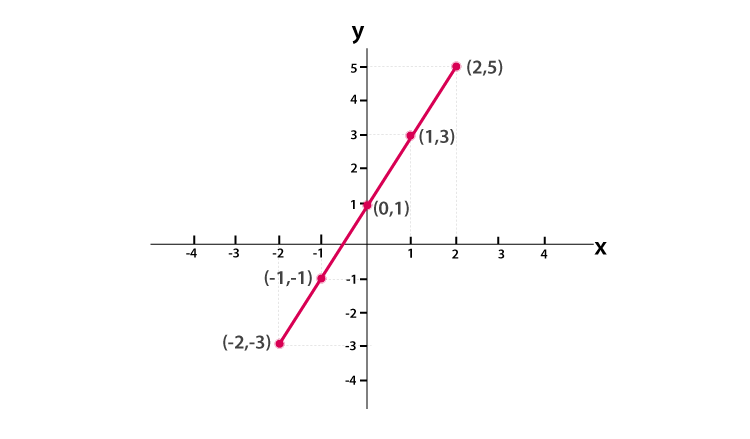
Linear Graph What Is Linear Graph
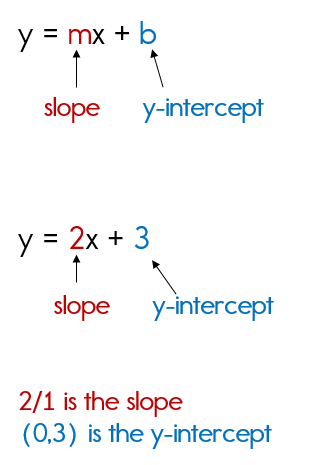
Graphing Using Slope Intercept Form
Linear Functions And Equations Zona Land Education

Misc 21 Line Y Mx 1 Is Tangent To Y2 4x If Value Of M Is

Y1 3 81 X1 1 X0 1 Y2 2 X2 2 K 1 Y3 2 25 X3 3 De Chegg Com

Various Forms Of Equation Of Line General Equation Videos Examples
How To Find The Equation Of A Straight Line Y Mx C Youtube
Plotting Graphs Y Mx C Mathscast Youtube
Slope Intercept Form Formula Examples Video Tutorial And Practice Problems With Explanation
Going From Standard Form To Slope Intercept Form
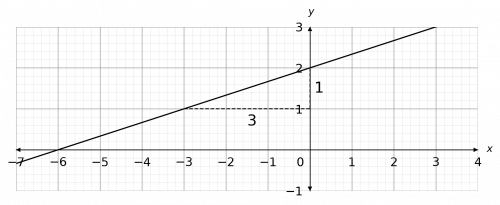
Y Mx C Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme

Straight Line Properties
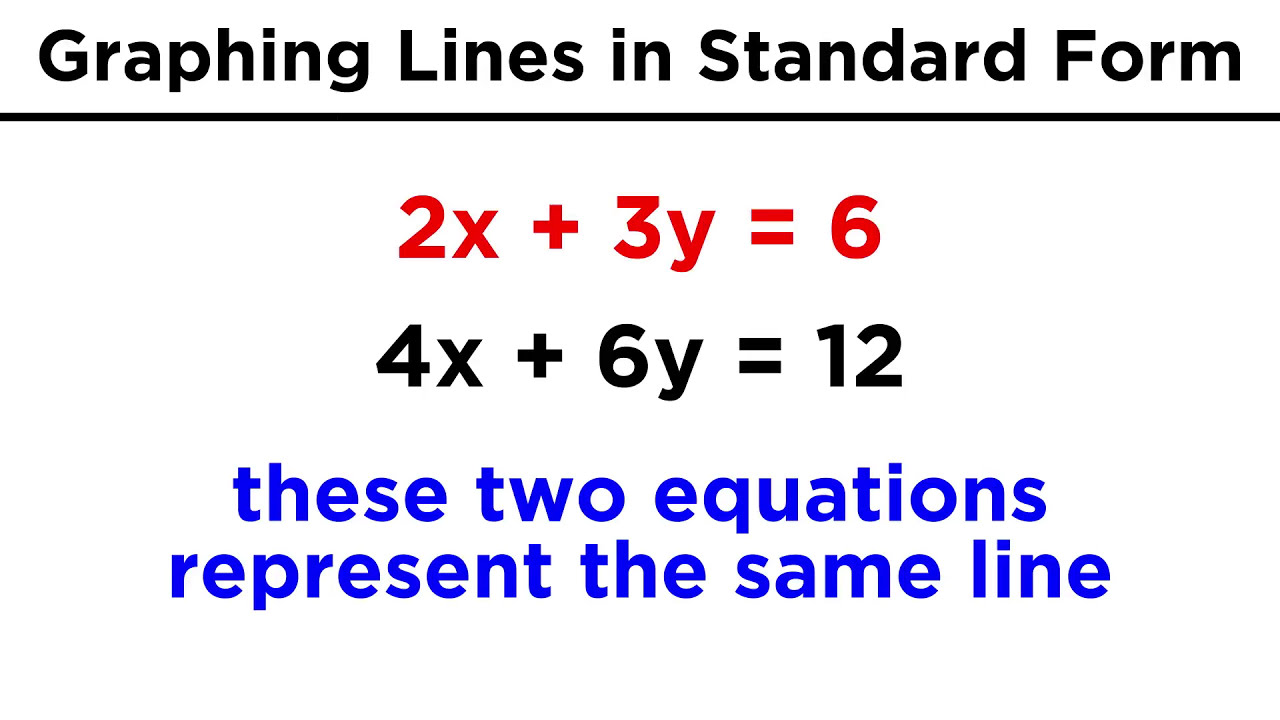
Graphing Lines In Standard Form Ax By C Youtube

Slope Of Lines Maths First Institute Of Fundamental Sciences Massey University
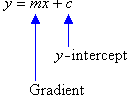
Equation Of A Straight Line
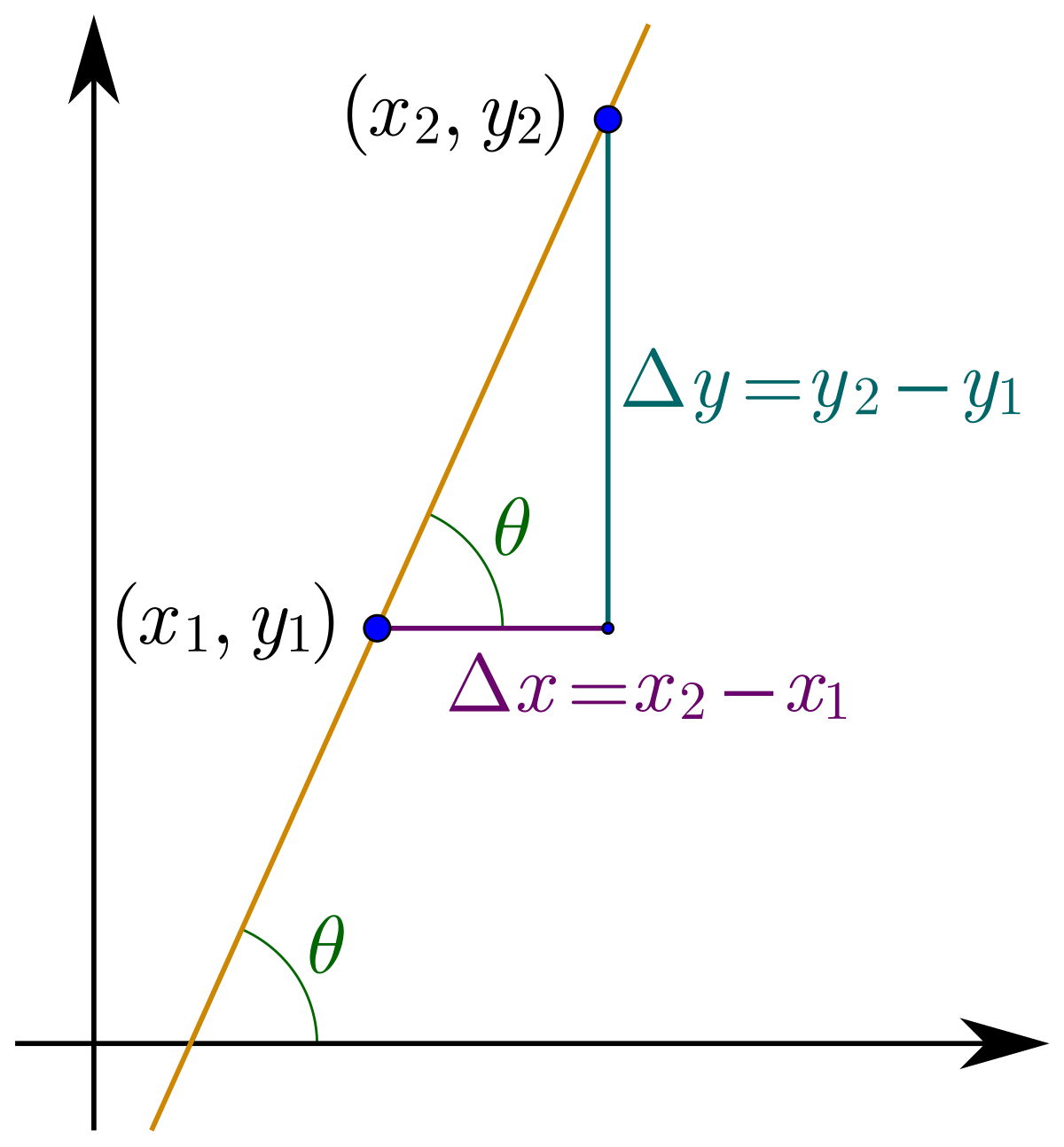
Slope Wikipedia

The Equation Of A Straight Line Y Mx C Youtube

What S The Y Intercept Virtual Nerd

Understanding Linear Regression With Python Practical Guide 2

Equation Of A Line Video Corbettmaths

Use The Slope Intercept Form Of An Equation Of A Line Elementary Algebra
Www Mun Ca Physics Undergraduates Fylabs P10 Manplotting Pdf

Y Mx C Math Resources Math Igcse Maths
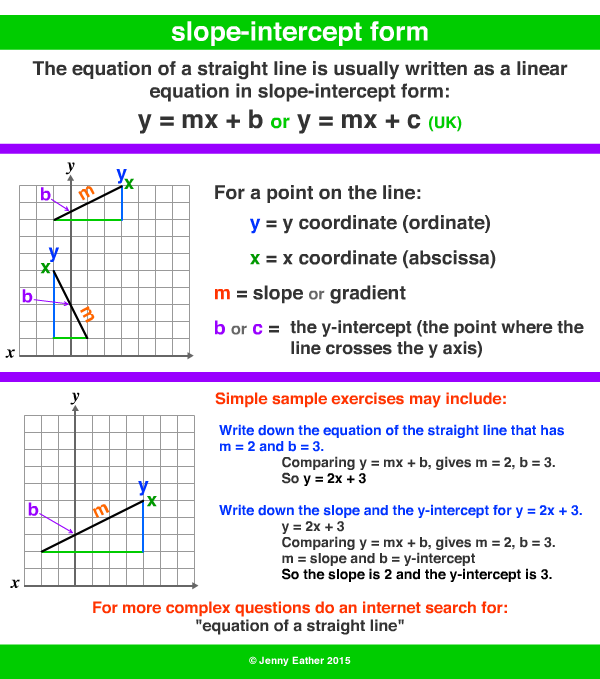
Equation Of A Straight Line A Maths Dictionary For Kids Quick Reference By Jenny Eather

Slope And Y Intercept From Equation Video Khan Academy
Y Mx C Equation Of A Line Youtube
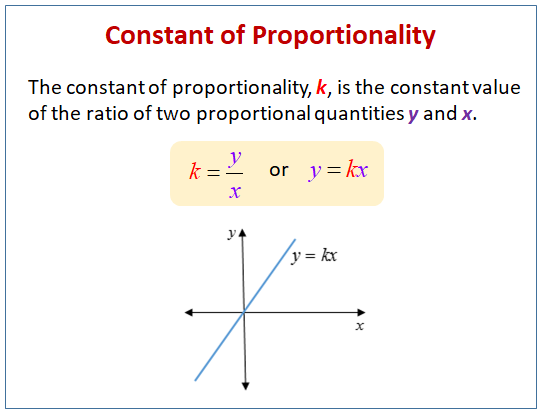
Constant Of Proportionality Solutions Examples Videos Worksheets Games Activities
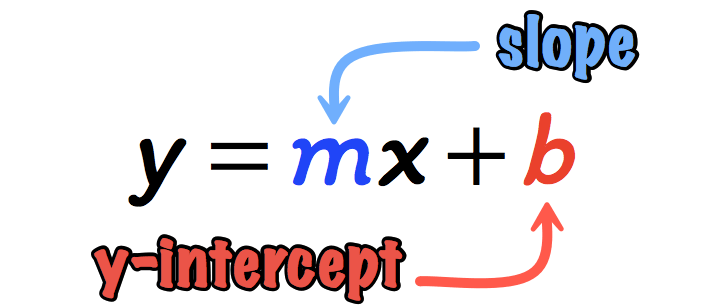
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath

Equation Of A Straight Line

Analyzing The Effects Of The Changes In M And B On The Graph Of Y Mx B Texas Gateway
Q Tbn And9gctxl4gvodwjgxazrj3yjrxvqm8utzfs3venblardl D0sur0qlf Usqp Cau

Gradient Slope Intercept Form Passy S World Of Mathematics
Q Tbn And9gctqfmfjd 6nalyteaouj0wwlmazf4gj6emtsqf0pkg Usqp Cau

Distance Of Point From A Line Meaning Formulas Videos And Examples
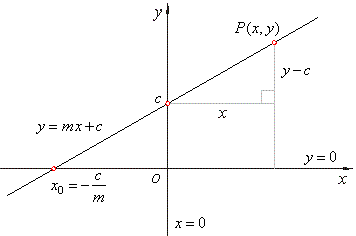
Linear Regression Using Gradient Descent By Adarsh Menon Towards Data Science
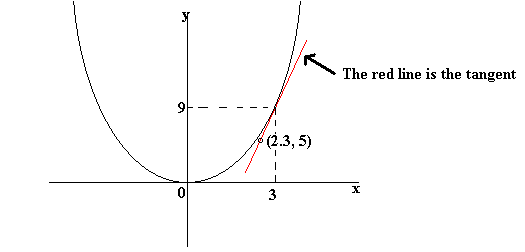
Gradients And Graphs Mathematics Gcse Revision
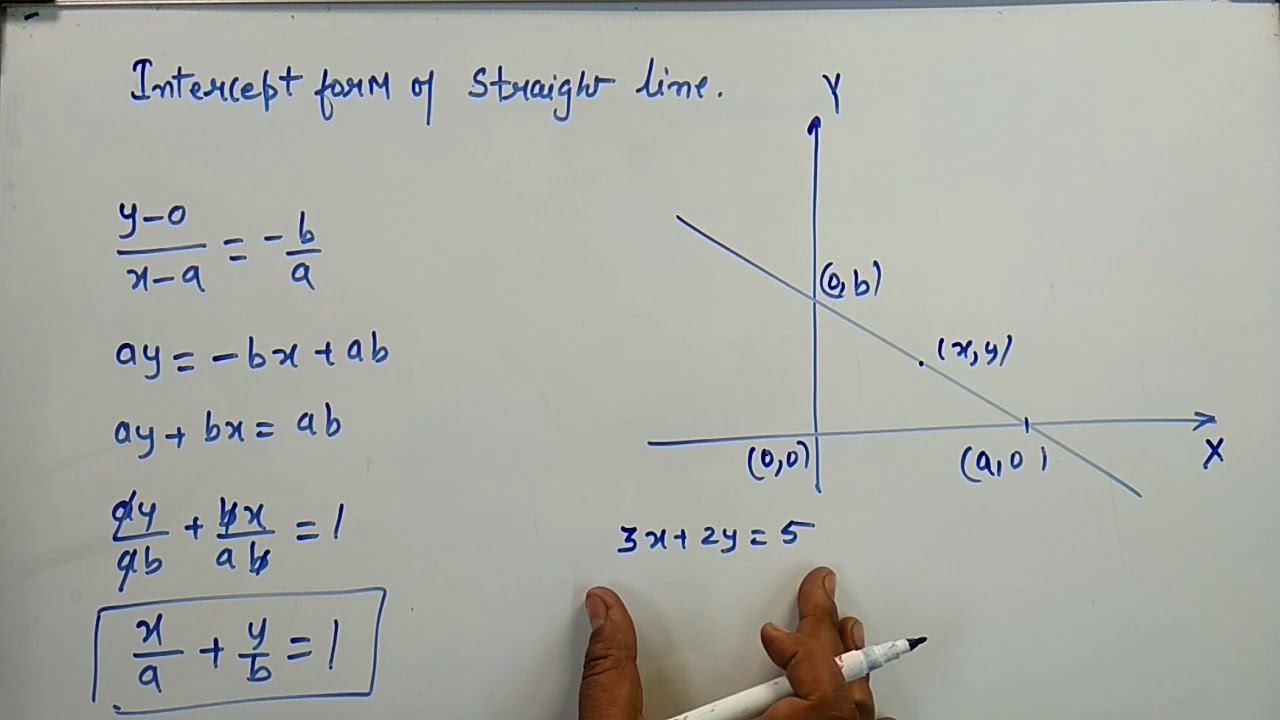
Deriving Intercept Form Of Straight Line X A Y B 1 Kamaldheeriya Youtube

Graphical Analysis Of One Dimensional Motion Physics

Mathematics For Machine Learning Linear Regression Least Square Regression By Daksh Deepak K Towards Data Science

Straight Lines Properties Relation Between Lines And Examples
Straight Line Graph Equation Explained Tessshebaylo
/math-equations-554974693-58a8db085f9b58a3c9229be2.jpg)
How To Determine The Equation Of A Line

Y Mx C

Misc 21 Line Y Mx 1 Is Tangent To Y2 4x If Value Of M Is
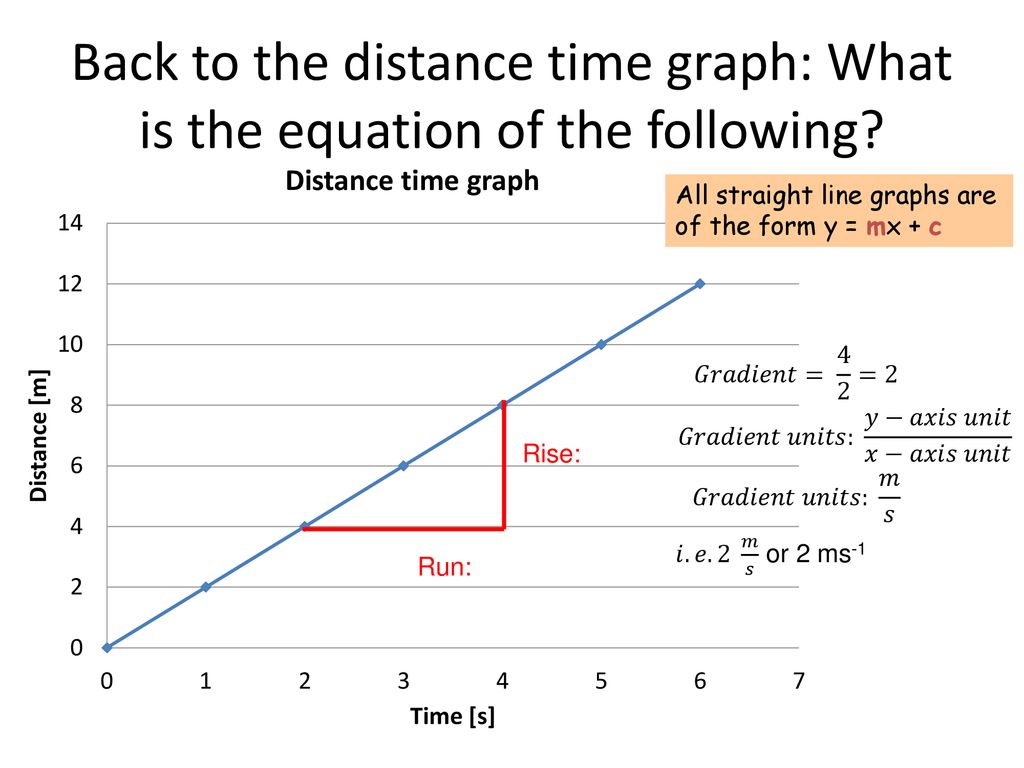
Graphs And Relationships Ppt Download

Arrhenius Equation Chemistry Video Clutch Prep

Equation Of A Straight Line

Y Mx B Lessons Blendspace
Www Mun Ca Physics Undergraduates Fylabs P10 Manplotting Pdf
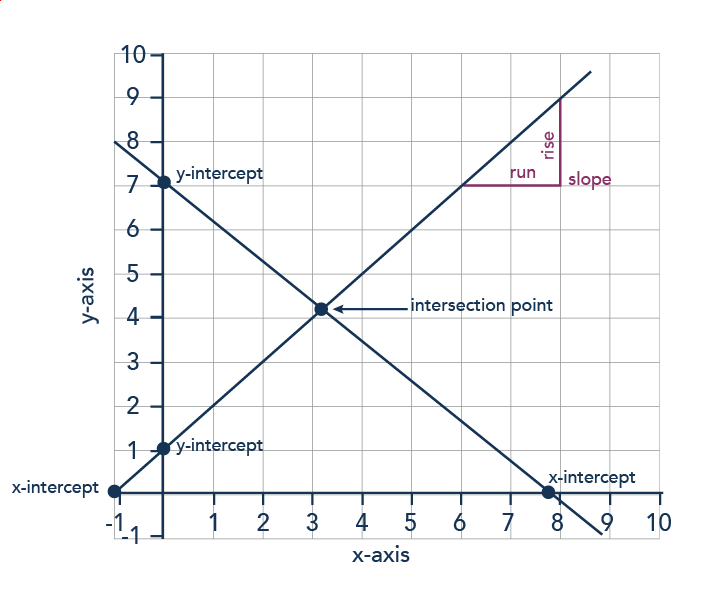
Creating And Interpreting Graphs Microeconomics
What Is The Graph Of Y Mx C Quora
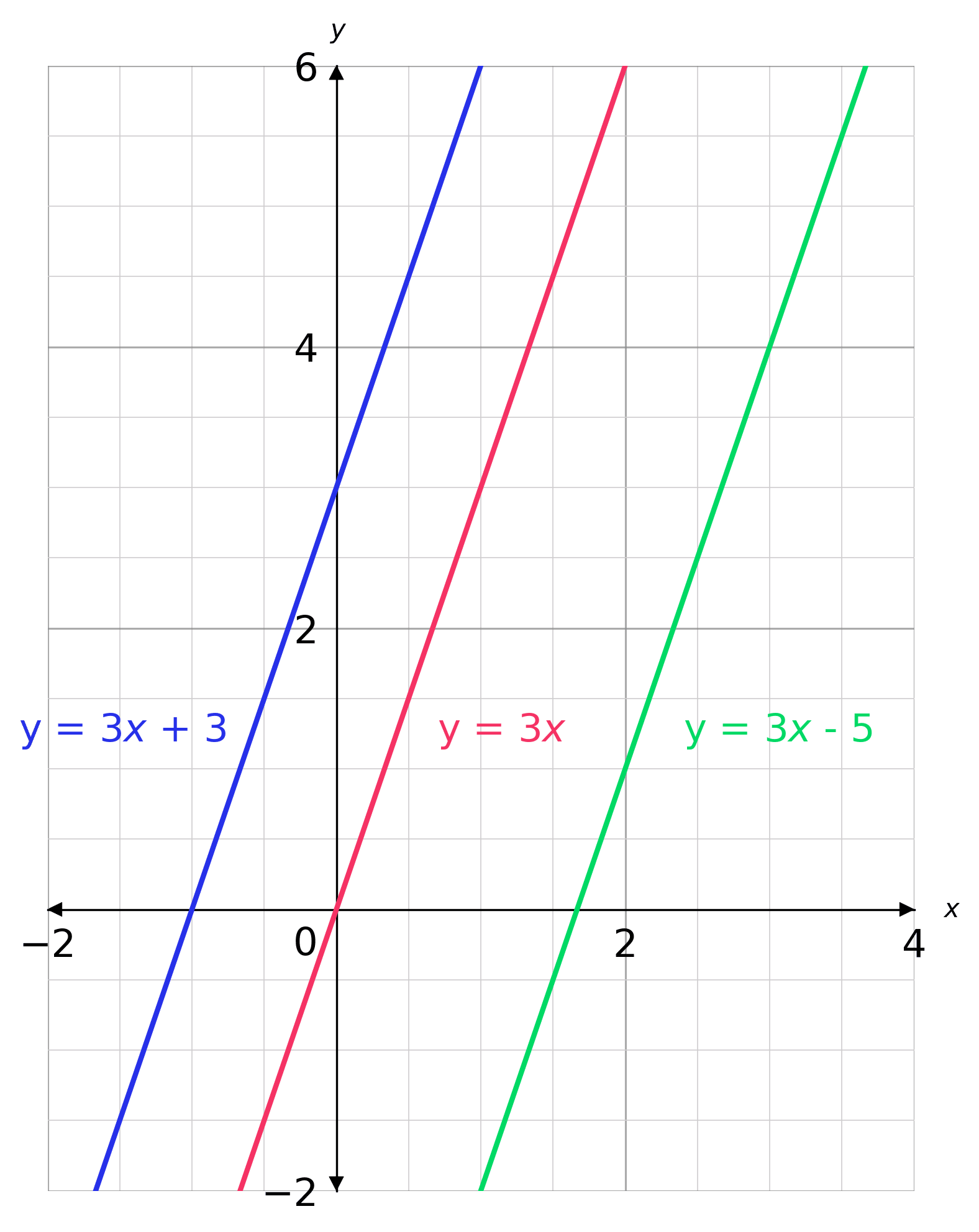
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Worksheets Questions And Revision
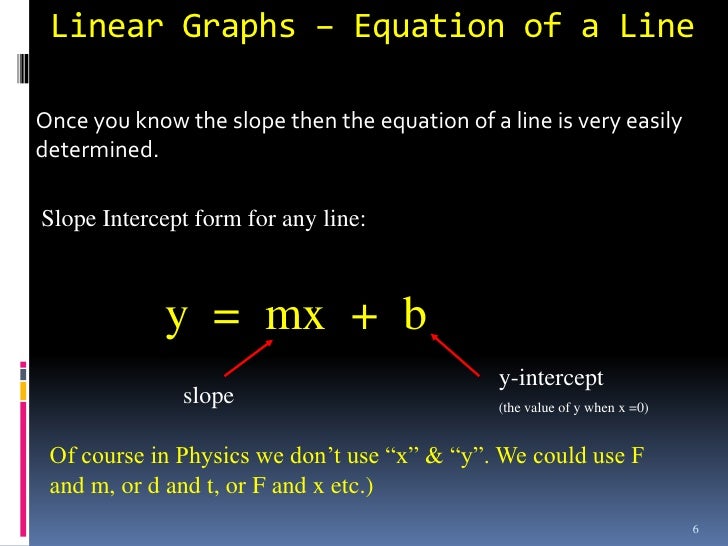
Graphs In Physics
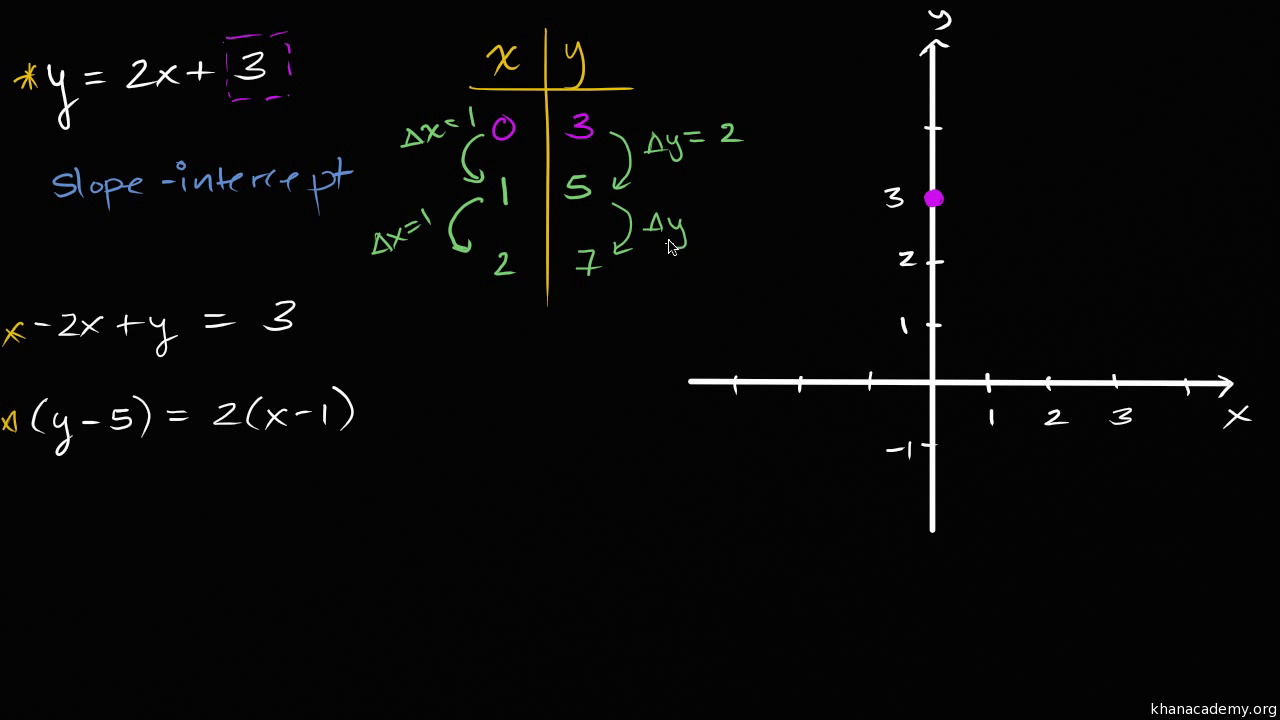
Intro To Slope Intercept Form Y Mx B Algebra Video Khan Academy
Perpendicular Distance From A Point To A Line

Ex 6 3 15 Find Equation Of Tangent Line To Y X2 2x 7
Y Mx C Well Explained Youtube
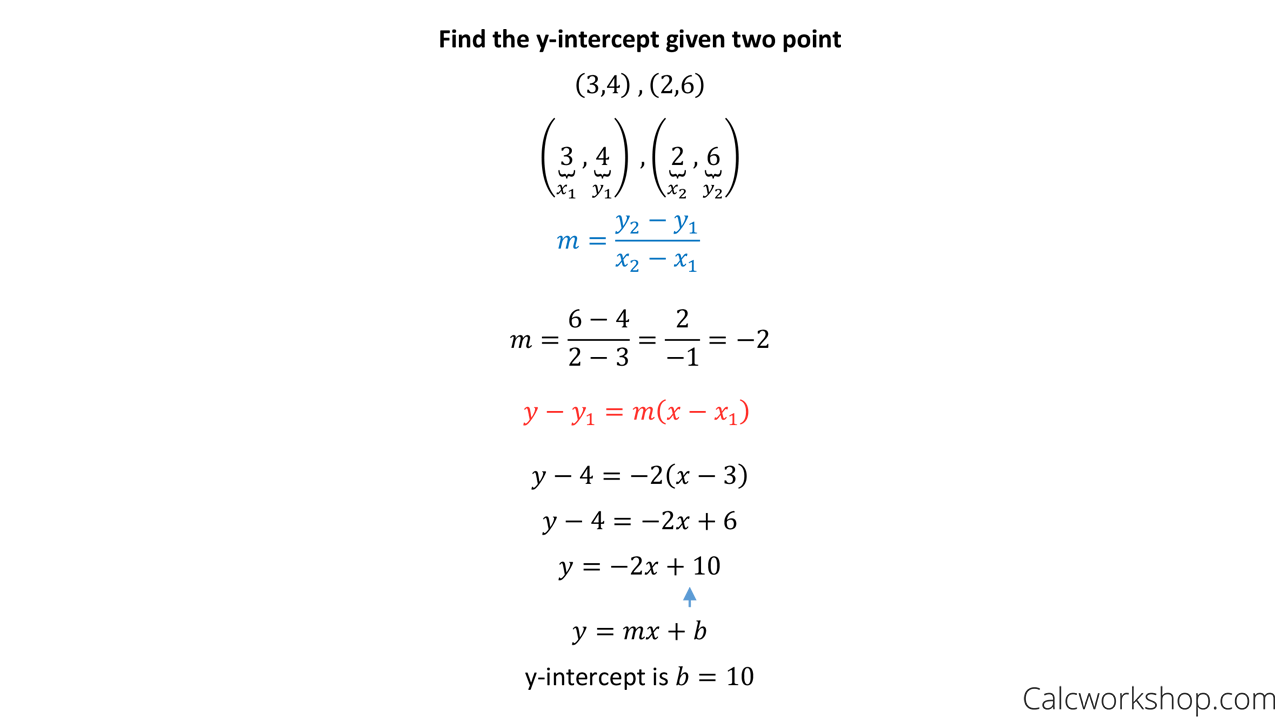
Point Slope Form Simply Explained W 17 Examples

Equation Of A Straight Line
Linear Equation Wikipedia
Graphing Slope Intercept Form Article Khan Academy

Y Mx C Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme
Y Mx C The Student Room
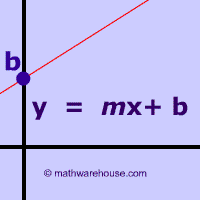
Slope Intercept Form Formula Examples Video Tutorial And Practice Problems With Explanation

Gradient Slope Intercept Form Passy S World Of Mathematics

Quadratic Function
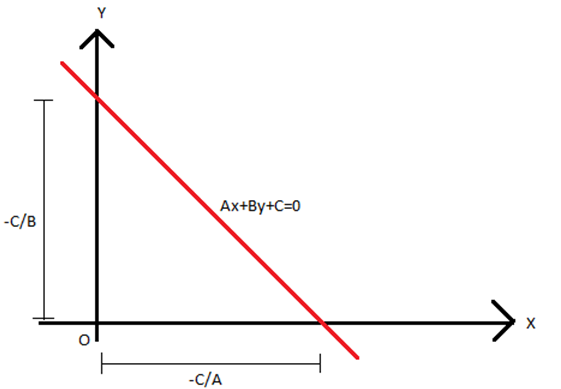
Equation Of A Line Straight Line Formulas Examples
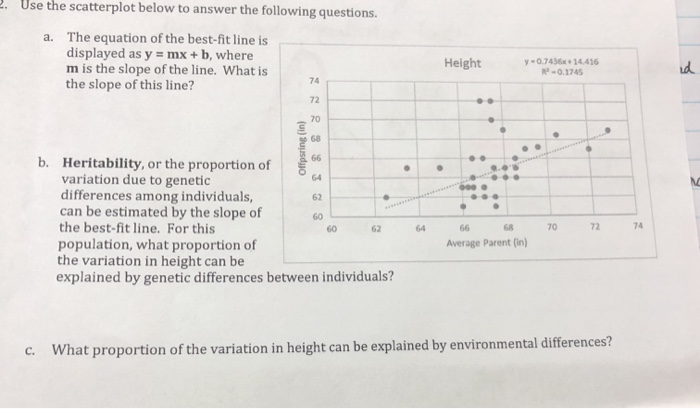
Solved 2 Use The Scatterplot Below To Answer The Followi Chegg Com
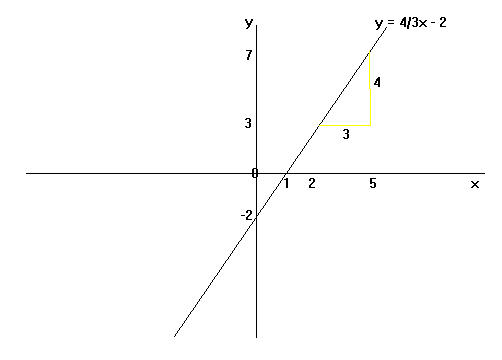
Equation Of A Straight Line Maths Gcse Revision

Gcse Maths What On Earth Is Y Mx C 67 Youtube

Linear Equations Intercepts Standard Form And Graphing Algebra Class Video Study Com

Gradient Slope Intercept Form Passy S World Of Mathematics
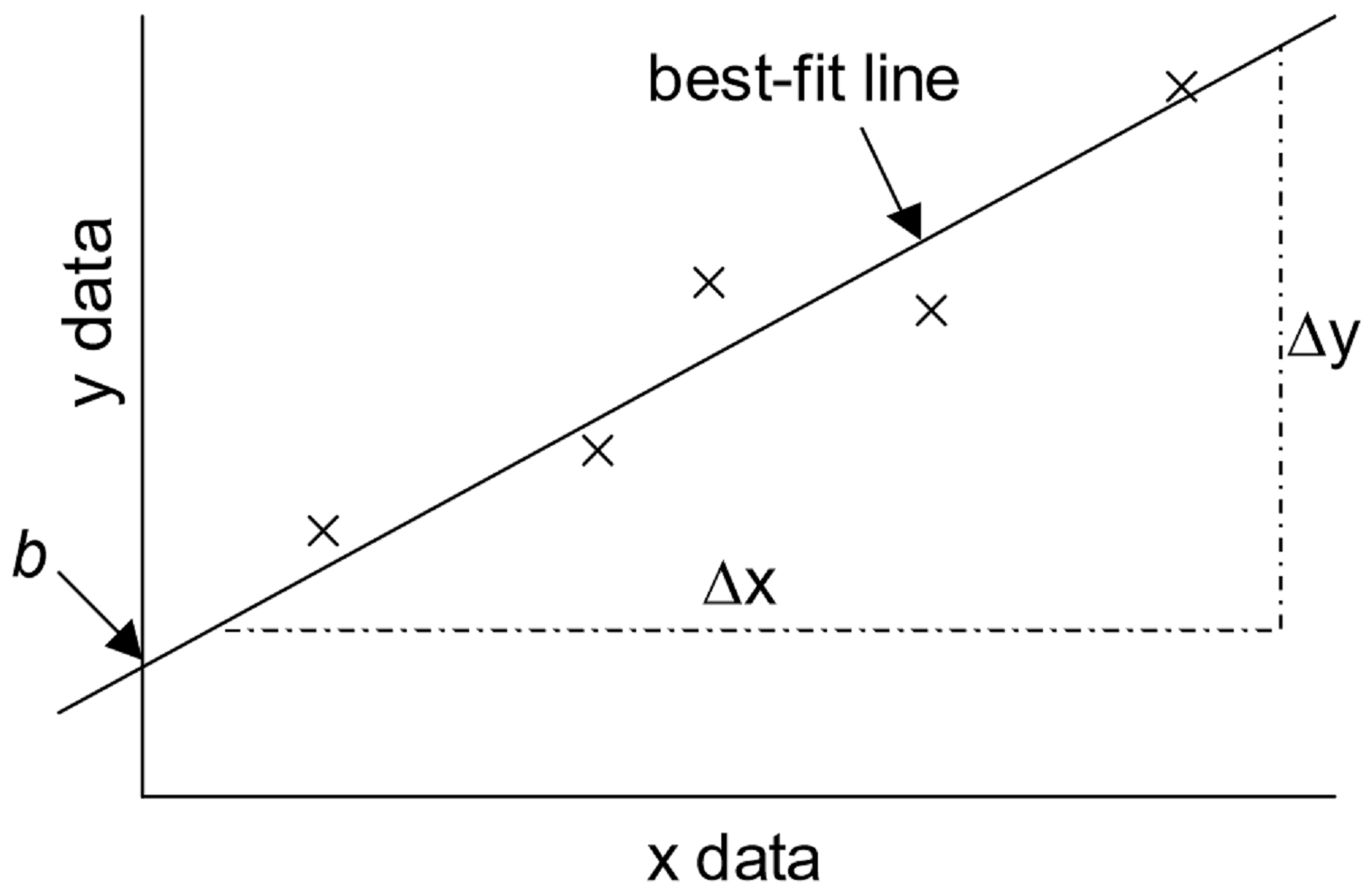
1 Using Excel For Graphical Analysis Of Data Experiment Chemistry Libretexts

Exercise Worksheet For Finding The Y Intercept From A Linear Equation
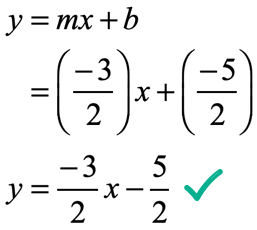
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath
What Is The Difference Between Slope Intercept And Standard Form Quora
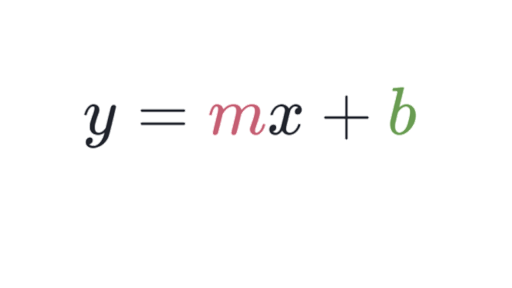
Slope Intercept Form Introduction Algebra Article Khan Academy

Distance Of Point From A Line Meaning Formulas Videos And Examples

Vector Equation Of A Line Read Calculus Ck 12 Foundation

Misc 21 Line Y Mx 1 Is Tangent To Y2 4x If Value Of M Is
Y Mx B Word Problems Worksheet Promotiontablecovers
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/LinearRelationshipDefinition2-a62b18ef1633418da1127aa7608b87a2.png)
Linear Relationship Definition
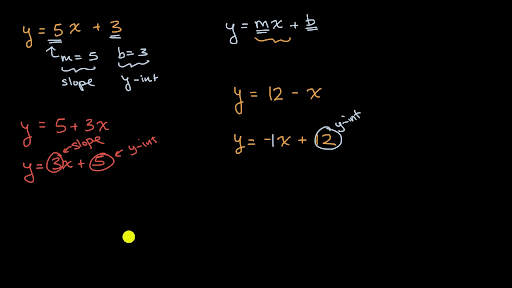
Slope And Y Intercept From Equation Video Khan Academy
What Is Y Mx C Quora
Equation Of A Straight Line
Intro To Slope Intercept Form Y Mx B Algebra Video Khan Academy
3

Graphing Parabolas

Equation Of A Straight Line

How To Find The Equation Of A Line 8 Steps With Pictures

Straight Lines Properties Relation Between Lines And Examples

Ks3 Mathematics A5 Functions And Graphs Ppt Download
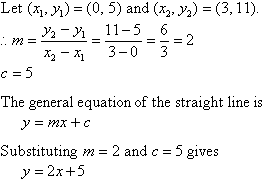
Equation Of A Straight Line

Unit 5 Section 2 Straight Line Graphs
Q Tbn And9gctx3b0iyyc87d1xce Eciibvadkvsxbvbk7rel7tdlzguykdhlv Usqp Cau

Interpreting The Slope Intercept Of A Linear Model Statistics Class Video Study Com
Gradients And Graphs Mathematics Gcse Revision
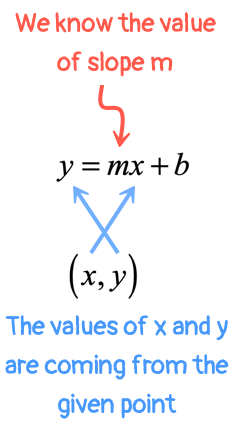
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath



