Solve The Formula Y Mx + B For M A C

Quadratic Function
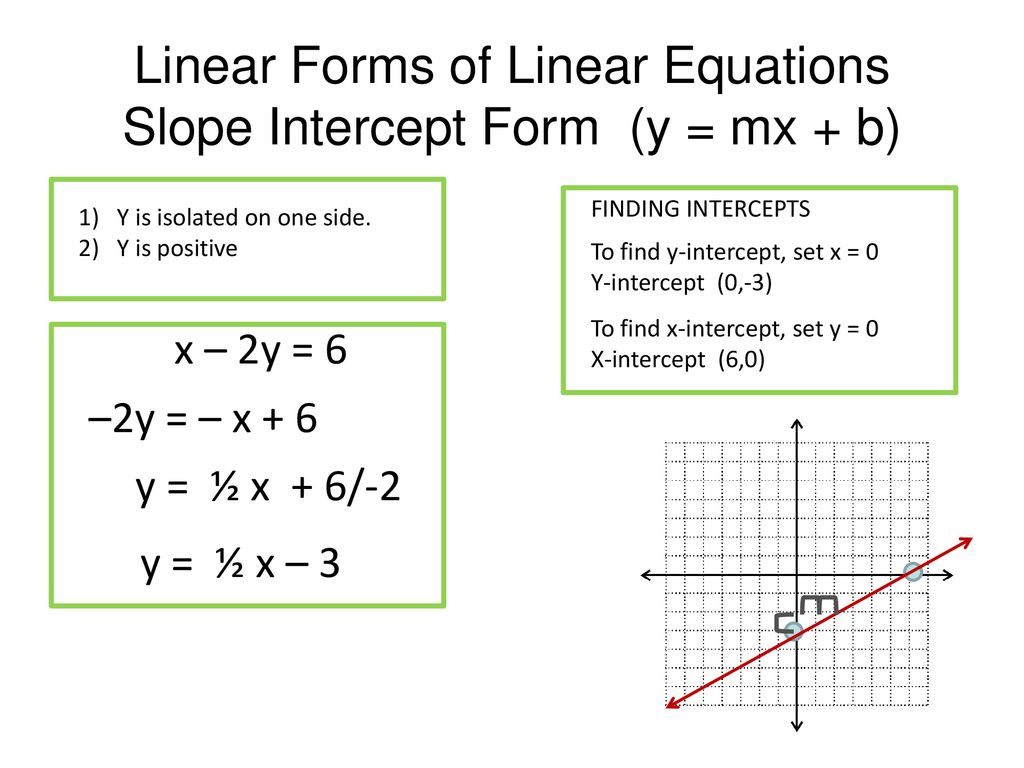
Solution A Express The Equation In The Form Y Mx B B Find The Slope And The Y Intercept And C Sketch The Graph Of The Linear Function Y 2 3 X 1

Slope And Y Intercept From Equation Video Khan Academy
What Is Y Mx C Quora
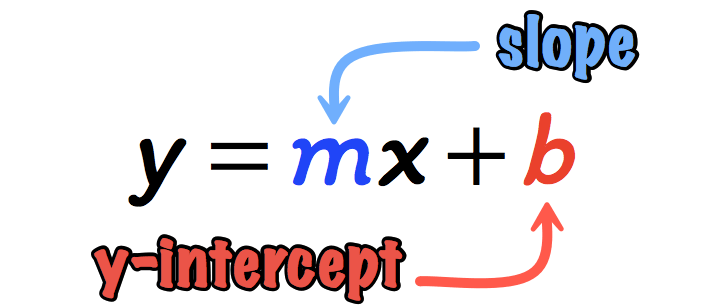
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath

Hw Solutions On Ohm S Law
By Dario Alejandro Alpern The purpose of this article is to show how to solve the Diophantine Equation Ax 2 Bxy Cy 2 Dx Ey F = 0The term Diophantine Equation means that the solutions (x, y) should be integer numbers For example, the equation 4y 2 y 25 = 0 has solutions given by the horizontal line y = 25, but since 25 is not an integer number, we will say that the equation.

Solve the formula y mx + b for m a c. Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep. Since for any relationship a=x^y, the relationship is invariant with respect to the numeric base you are using (base 2, base 6, base 16, etc) Since the mod N operation is equivalent to extracting the least significant digit (LSD) in base N Since the LSD of the result A in base N can only be affected by the LSD of X in base N, and not digits in higher places. Key Takeaways The graph of any quadratic function f (x) = a x 2 b x c, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0, is called a parabola;.
(2) Students recognize equations for proportions (y/x =m or y = mx) as special linear equations (y = mx b) understanding that t he constant of proportionality (m) is the slope, and the graphs are lines through the origin They understand that the slope (m) of a line is a constant rate of change, so that if the input or. The slopeintercept form of a linear equation is y = mx b, where x and y are coordinates of an ordered pair, m is the slope of the line, and b is where the line crosses the yaxis Which is an equivalent equation solved for the slope, m?. Free solve for a variable calculator solve the equation for different variables stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy.
Determine slope from the two given points using the formula Determine the yintercept (b) by using substitute a point for the x and y variables substitute the slope for the m variable solve for b Rewrite the equation by replacing the m and b variables with the values you found. Cancelling 75 with 3 times 25 and applying the formula of a m /a n = a mn → 3*10 4(4) → 3*10 8 Problem 2 Find x if 3 2x1 3 2x1 = 270 Solution Taking out a term common, we get → 3 2x1 (13 2) Observe that here, we applied the formula a mn = a ma n in writing 3 2x1 as a product of 3 2x1 and 3 2 → 3 2x1 (10) = 270 → 3. An equation of the form y = mx b which fits the above description with B =1,A = m and C = b If B = 0, we can rearrange the equation to the form given below describing a vertical line ) If the line is vertical, all of the x values on the line are the same (see example below) and its equation.
Writing m = log 10 a and c = b log 10 a, the equation becomes y = mx c which represents a straight line with gradient m and yintercept c Hence, plotting log 10 y against x should approximately produce a straight line and the values of m, c and hence a, b are relatively easy to estimate This is a very powerful and clever application of logarithms, that is used widely in experimental science. Entries given by the jth row of B The product C = AB is the m×p matrix defined by c ij = r i(A),c j(B)X where r i(A) is the vector in R n consisting of the ith row of A and similarly c j(B) is the vector formed from the jth column of B Other notation for C = AB c ij = n k=1 a ikb kj 1 ≤i ≤m 1 ≤j ≤p Example 212 Let A =} 101 321. For an equation of the form \(ax^2bxc=0\), you can solve for x using the Quadratic Formula $$ x = \frac{b \pm \sqrt{b^24ac}}{2a} $$ Binomial Theorem \((ab)^1= a b\) \((ab)^2=a^22abb^2\) \((ab)^3=a^33a^2b3ab^2b^3\) \((ab)^4=a^44a^3b6a^2b^24ab^3b^4\) Difference of Squares.
The m is the slope of the line And b is the b in the point that is the yintercept (0, b) For example, for the equation y = 3x – 7, the slope is 3, and the yintercept is (0, −7) What if the equation is written as 2y = 5x 1?. Solve for m y=mxb y = mx b y = m x b Rewrite the equation as mxb = y m x b = y mxb = y m x b = y Subtract b b from both sides of the equation mx = y −b m x = y b Divide each term by x x and simplify Tap for more steps Divide each term in m x = y − b m x = y b by x x. Y = mx c In Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Brazil, China, Czech Republic, Denmark, Ethiopia, France, Lebanon, Netherlands, Kosovo, Kyrgyzstan, Norway, Poland, Romania, South Korea, Surinam, Spain, Tunisia and Viet Nam y = ax b In Azerbaijan, China, Finland, Russia and Ukraine y = kx b In Greece ψ = αχ β In Italy y = mx q In Japan y = mx d.
Modular inverse is used to solve $$(A / B) \% M$$ as follows $$(A / B) \% M = (A * B^{1}) \% M$$ After you find the inverse, you can solve this equation easily Contributed by Shubham Gupta View all comments. Then the law of cosines states a 2 = c 2 b 2 2bc cos A, solving for cos A, cos A = ( b 2 c 2 a 2) / 2bc b 2 = a 2 c 2 2ca cos B, solving for cos B, cos B = ( c 2 a 2 b 2) / 2ca. First, subtract b from the right, but in doing so, you must also subtract b from the left, once this step is complete your equation looks like y b = mx now divide the right side by m to free up.
Solve for x y=mxb Rewrite the equation as Subtract from both sides of the equation Divide each term by and simplify Tap for more steps Divide each term in by Cancel the common factor of Tap for more steps Cancel the common factor Divide by Move the negative in front of the fraction. Slope Intercept Form Equation y = mx b, or sometimes y = mx c, m = slope (the amount of rise over run of the line) b= yaxis intercept ( where the line crosses over the yaxis) To calculate the slope intercept form equation from two coordinates (x 1,y 1) and (x 2,y 2). The discriminant for any quadratic equation of the form $$ y =\red a x^2 \blue bx \color {green} c $$ is found by the following formula and it provides critical information regarding the nature of the roots/solutions of any quadratic equation.
Y=mxc Take c from both sides yc = mx Divide both sides by m (yc) / m =x Now swap sides to make it prettier x = (yc) / m. For a quadratic equation ax 2 bx c = 0 where a ≠ 0, the roots will be given by the equation as \(x=\frac{b\pm \sqrt{b^{2}4ac}}{2a}\) Δ = b 2 − 4ac is called the discriminant;. 34 CauchyEuler Equation 45 Type Roots Form of y c I m 1 6 = m 2 (real and different) y = c 1 x m 1 c 2 x m 2 II m 1 = m 2 (real and equal) y = c 1 x m 1 c 2 x m 1 ln x III m = a ± ib y = x a c 1 cos (b ln x) c 2 sin (b ln x) (Conjugate complex roots ) Example 318 Solve the differential equation x 2 y 002 y = 0.
Entries given by the jth row of B The product C = AB is the m×p matrix defined by c ij = r i(A),c j(B)X where r i(A) is the vector in R n consisting of the ith row of A and similarly c j(B) is the vector formed from the jth column of B Other notation for C = AB c ij = n k=1 a ikb kj 1 ≤i ≤m 1 ≤j ≤p Example 212 Let A =} 101 321. To solve for m we want to get m by itself on one side of the equals sign, with everything else on the other side First we subtract b from both sides, to get it out of the right side of the equation y b = mx b b y b = mx Now we divide both sides by x, to get m completely by itself (yb)/x = (mx)/x (yb)/x = m So m is equal to (yb)/x. Algebra Formulas A basic formula in Algebra represents the relationship between different variables The variable could be taken as x, y, a, b, c or any other alphabet that represents a number unknown yet Example – (x y = z) (a b)2=a2 2ab b2 (a−b)2=a2−2ab b2 (a b)(a –.
Then you must rewrite the equation in the form y = mx b Solve for y 2y = 5x 1 y = d ivide both sides of. Writing m = log 10 a and c = b log 10 a, the equation becomes y = mx c which represents a straight line with gradient m and yintercept c Hence, plotting log 10 y against x should approximately produce a straight line and the values of m, c and hence a, b are relatively easy to estimate This is a very powerful and clever application of logarithms, that is used widely in experimental science. 0 = Ax By C Let A = 2, B = 3, C = 4 So 0 = 2x 3y 4 slope = m = A/B = 2/3 = 067 (approximately) yintercept = b = C/B = 4/3 = 133 (approximately) Our line in slopeintercept form y = mx b y = 067x (133) or y = 067x 133.
A leastsquares solution of the matrix equation Ax = b is a vector K x in R n such that y = Mx B If our three data points were to lie on this line, then the following equations would be satisfied Putting our linear equations into matrix form, we are trying to solve Ax = b for A = C 01 11 21 D x = L M B M b = C 6 0 0 D. For nonreal roots, Δ < 0;. A leastsquares solution of the matrix equation Ax = b is a vector K x in R n such that y = Mx B If our three data points were to lie on this line, then the following equations would be satisfied Putting our linear equations into matrix form, we are trying to solve Ax = b for A = C 01 11 21 D x = L M B M b = C 6 0 0 D.
(2) Students recognize equations for proportions (y/x =m or y = mx) as special linear equations (y = mx b) understanding that t he constant of proportionality (m) is the slope, and the graphs are lines through the origin They understand that the slope (m) of a line is a constant rate of change, so that if the input or. When graphing a parabola always find the vertex and the yinterceptIf the xintercepts exist, find those as wellAlso, be sure to find ordered pair solutions on either side of the line of symmetry, x = − b 2 a Use the leading coefficient, a, to. Substitute m for a, 10m for b, and 25my for c in the quadratic formula, \frac{b±\sqrt{b^{2}4ac}}{2a} This equation is in standard form a x 2 b x c = 0 Substitute m for a , 1 0 m for b , and 2 5 m − y for c in the quadratic formula, 2 a − b ± b 2 − 4 a c.
If a, b and c are the lengths of the legs of a triangle opposite to the angles A, B and C respectively;. In terms of coordinate geometry, a parabola is a curve whose (x, y)coordinates are described by a seconddegree polynomial, ie any equation of the form = = , where p represents the polynomial of degree 2 and a 0, a 1, and a 2 ≠ 0 are constant coefficients whose subscripts correspond to their respective term's degree The geometrical interpretation of the quadratic formula is that it. They use knowledge, eg, formulas (relations) Pythagorean theorem, Sine theorem, Cosine theorem, Heron's formula, solving equations and systems of equations The second stage is the calculation of the properties of the triangle from the known lengths of its three sides Examples of how to enter a triangle.
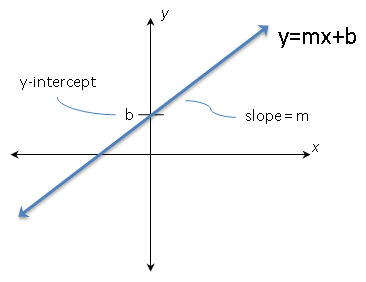
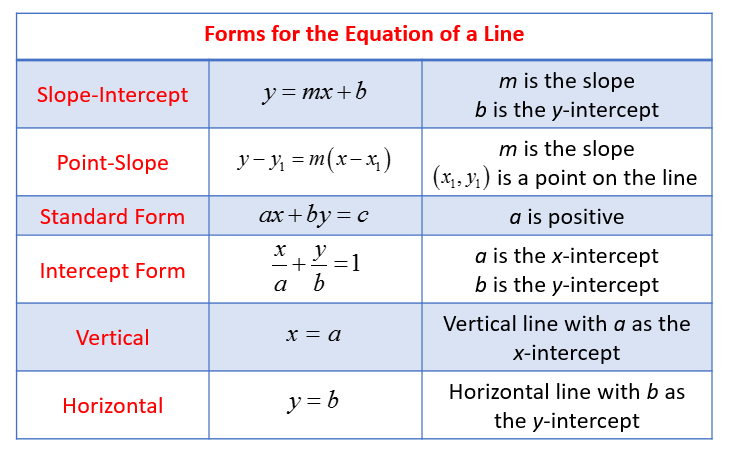
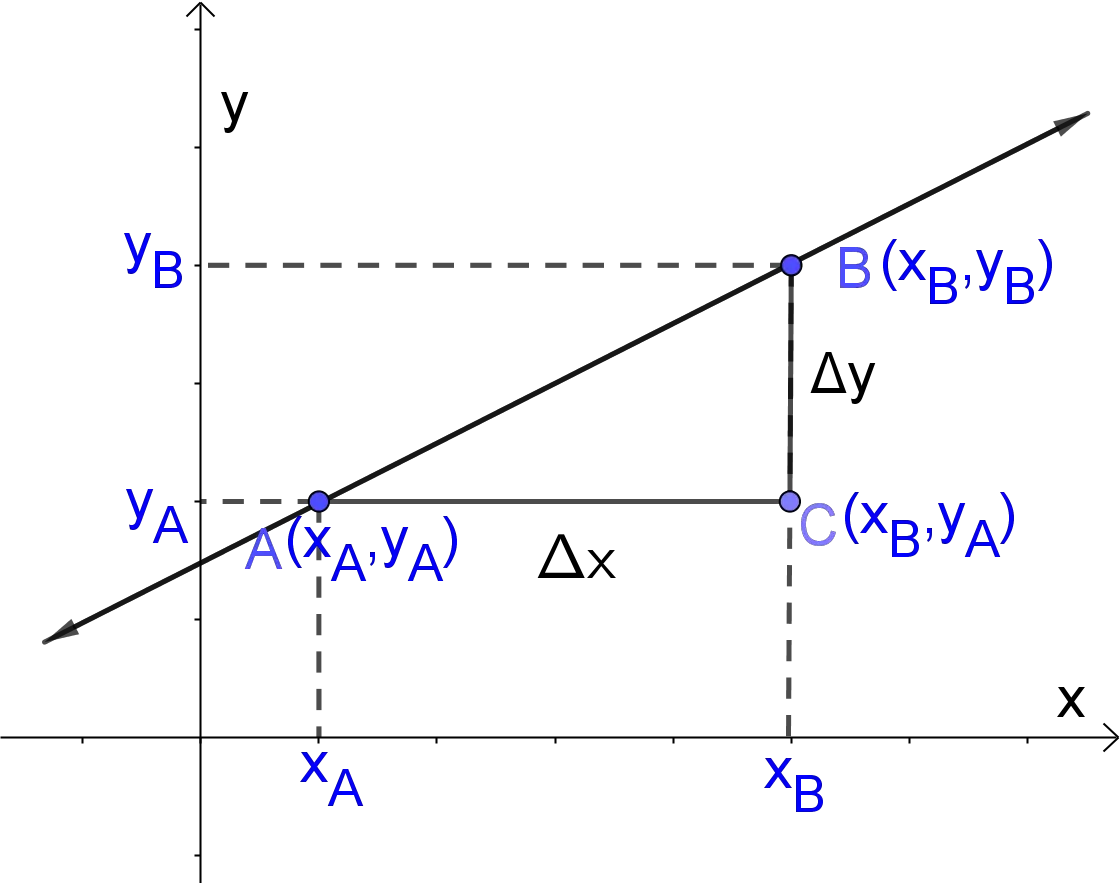
Y = mx b Solve for m m= (y b)/x Standard Form Ax By = C Surface Area of a Sphere SA= 4πr² Solve for π π = SA/(4r²) Interest formula I = prt solve for r r = I/(pt) Volume of a cone V = (Ah)/3 Solve for h h = (3v)/A Area of a trapezoid A= (h/2)(a b) Solve for b b = (2A)/h a OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR Angle Measures 14. Slope Slope of the line containing the two points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is y2 − y1 rise = x2 − x1 run Slope – intercept form The equation of the line with slope m and yintercept ( 0,b ) is y = mx b Point – Slope form The equation of the line with slope m and passing through the point ( x1 , y1 ) is m= y = y1 m ( x − x1. 34 CauchyEuler Equation 45 Type Roots Form of y c I m 1 6 = m 2 (real and different) y = c 1 x m 1 c 2 x m 2 II m 1 = m 2 (real and equal) y = c 1 x m 1 c 2 x m 1 ln x III m = a ± ib y = x a c 1 cos (b ln x) c 2 sin (b ln x) (Conjugate complex roots ) Example 318 Solve the differential equation x 2 y 002 y = 0.
Mx = a(1/c b/y) There are a few ways to tackle this I want to get rid of all fractions first, so let's distribute the "a" into both terms on the right side, then multiply both sides by the LCD of "cy" mx = a/c ab/y cmxy = ay abc Now subtract "abc" from both sides so all terms with "c" in it are on the same side cmxy abc = ay. For real and coincident roots, Δ = 0;. Y = mx b Solve for m m= (y b)/x Standard Form Ax By = C Surface Area of a Sphere SA= 4πr² Solve for π π = SA/(4r²) Interest formula I = prt solve for r r = I/(pt) Volume of a cone V = (Ah)/3 Solve for h h = (3v)/A Area of a trapezoid A= (h/2)(a b) Solve for b b = (2A)/h a OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR Angle Measures 14.
If the polynomial is divided by one of its roots, we will get zero as the remainder in the last step Then, the polynomial will be reduced to a quadratic equation of the form Ax2BxC=0 where A is a, B is bnew and C is cnew Then the quadratic equation is solved Now, we have all 3 roots of the equation. If α and β are the two roots of the equation ax 2 bx. Since for any relationship a=x^y, the relationship is invariant with respect to the numeric base you are using (base 2, base 6, base 16, etc) Since the mod N operation is equivalent to extracting the least significant digit (LSD) in base N Since the LSD of the result A in base N can only be affected by the LSD of X in base N, and not digits in higher places.
Determine slope from the two given points using the formula Determine the yintercept (b) by using substitute a point for the x and y variables substitute the slope for the m variable solve for b Rewrite the equation by replacing the m and b variables with the values you found. A −2 ≤ w ≤ 3 c w ≥ 3 and w < −2 b −2 < w ≤ 3 d −2 > w ≥ 3 ____ 33 Solve y = mx b for m a m = y − b x c m = y bx b m = x y − b d m = y b x ____ 34 Write an equation for the line that contains the point (1, 2) and is perpendicular. Every Month we have a new GIVEAWAY that is FREE to Enter See link below for detailshttps//wwwminutemathtutorcom/currentgiveawaySolve For The Given Vari.
B 5y 3 d 5 3 y ____ 32 Which inequality is shown by the graph below?. Solve a formula for a given variable Use Polya's four step process to solve word problems involving formulas Introduction In this tutorial we will be solving problems using formulas to help us In Tutorial 8 An Introduction to Problem Solving, we had to create our own equations based on the given information However, all of the problems we. Notice that for a linear equation, if uis a solution, then so is cu, and if vis another solution, then u vis also a solution In general any linear combination of solutions c 1u 1(x;y) c 2u 2(x;y) c nu n(x;y) = i=1 c iu i(x;y) will also solve the equation The linear equation (19) is called homogeneous linear PDE, while the equation.
For real and distinct roots, Δ > 0;.
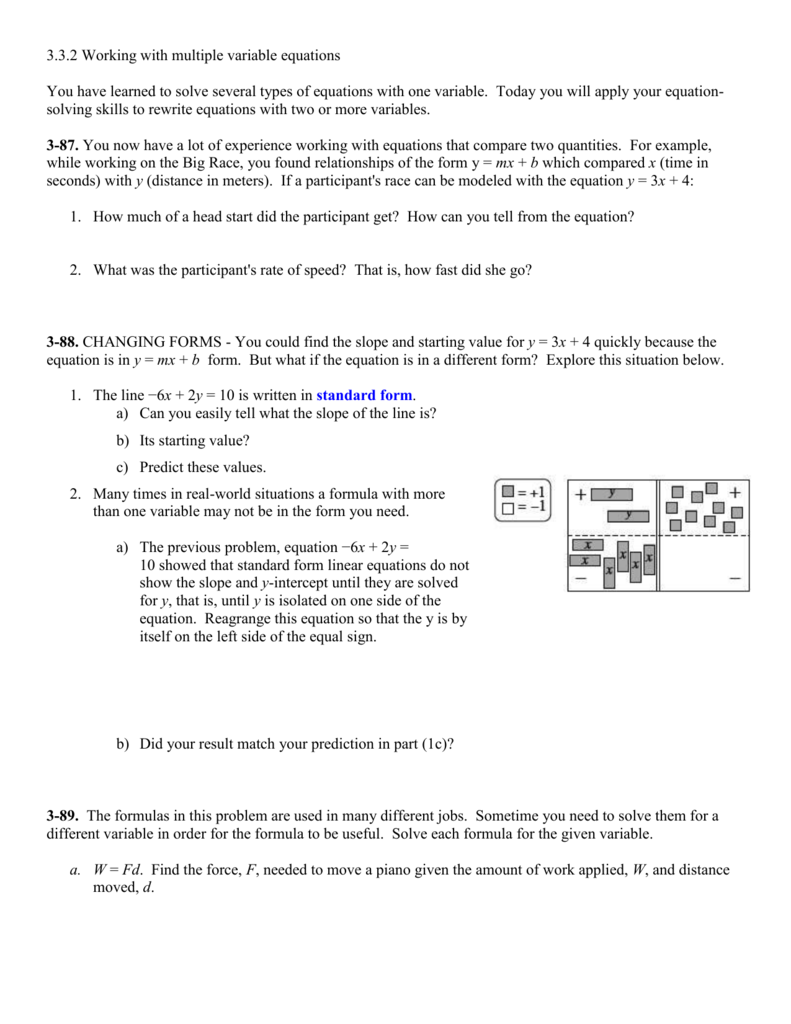
Notes 3 3 2
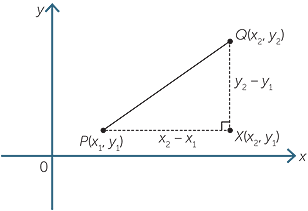
Introduction To Coordinate Geometry

How To Find The Perpendicular Bisector Of Two Points 8 Steps
Chapter 4
Q Tbn And9gctqfmfjd 6nalyteaouj0wwlmazf4gj6emtsqf0pkg Usqp Cau
How To Find B In Linear Equation Form Y Mx B If The 2 Coordinates Are 5 6 And 1 0 Socratic

How To Find The Equation Of A Line 8 Steps With Pictures
What Is Y Mx C Quora

Finding Linear Equations
Intro To Slope Intercept Form Y Mx B Algebra Video Khan Academy

Y Mx B What Does The M And B Represent Ppt Video Online Download
Find Slope And Y Intercept From Equation Expii

Question Video Finding The Equation Of A Line Passing Through Two Points Nagwa

Solved Rewrite The Slope Intercept Formula Y Mx B For T Chegg Com
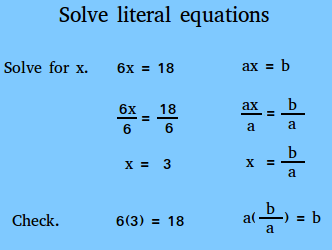
How To Solve Literal Equations
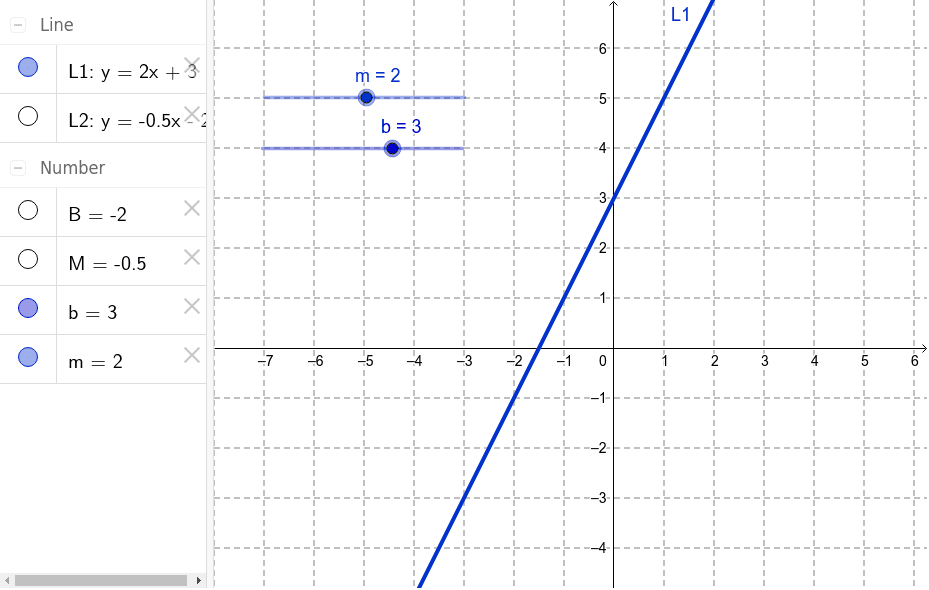
Linear Equations Y Mx B Geogebra

Nts

Graphing In Y Mx B Format Rlas 8th Grade Math

Gradient Slope Intercept Form Passy S World Of Mathematics

Question Video Writing Linear Equations In Standard Form Nagwa
Linear Equation Wikipedia

6 Ways To Use The Slope Intercept Form In Algebra Wikihow

How To Convert Non Linear Equations To Linear Form Y Mx C Youtube
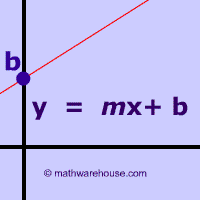
Slope Intercept Form Formula Examples Video Tutorial And Practice Problems With Explanation

Module 1 Linear Functions

Y Mx B Poster Zazzle Com In 21 Multiplication Chart Teaching Math Poster
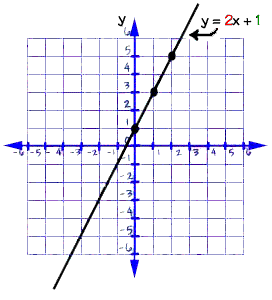
Graphing Equations And Inequalities Slope And Y Intercept First Glance
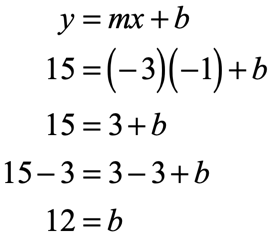
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath
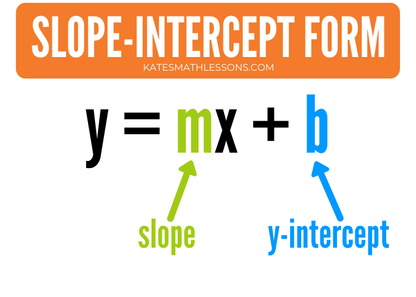
Using Two Points To Write An Equation In Slope Intercept Form Kate S Math Lessons
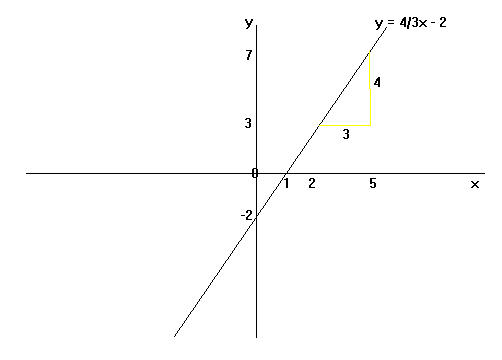
Equation Of A Straight Line Maths Gcse Revision

Solved Find The Equations For The Lines Through The Point Chegg Com
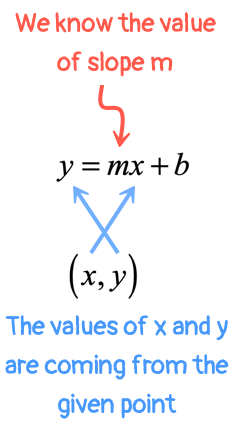
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath
1

Equation Of A Straight Line

Vertex Form Equation Functions Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
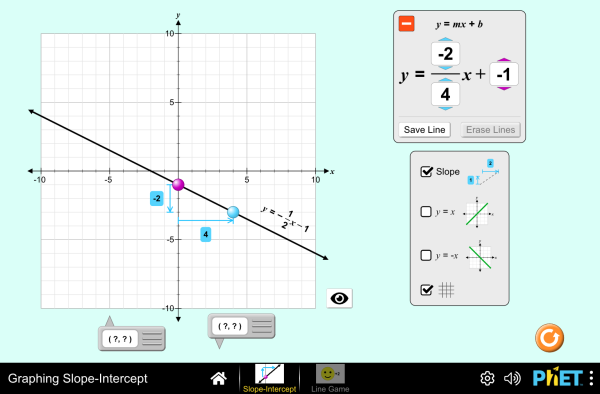
Graphing Slope Intercept Slope Intercept Form Graphing Linear Equations Phet Interactive Simulations
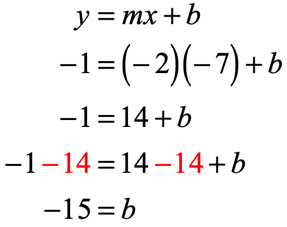
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath

3 Ways To Find The Y Intercept Wikihow

Analyzing The Effects Of The Changes In M And B On The Graph Of Y Mx B Texas Gateway
Converting To Slope Intercept Form Video Khan Academy
Finding The Equation Of A Line From A Graph Y Mx B Youtube

Equation Of A Straight Line
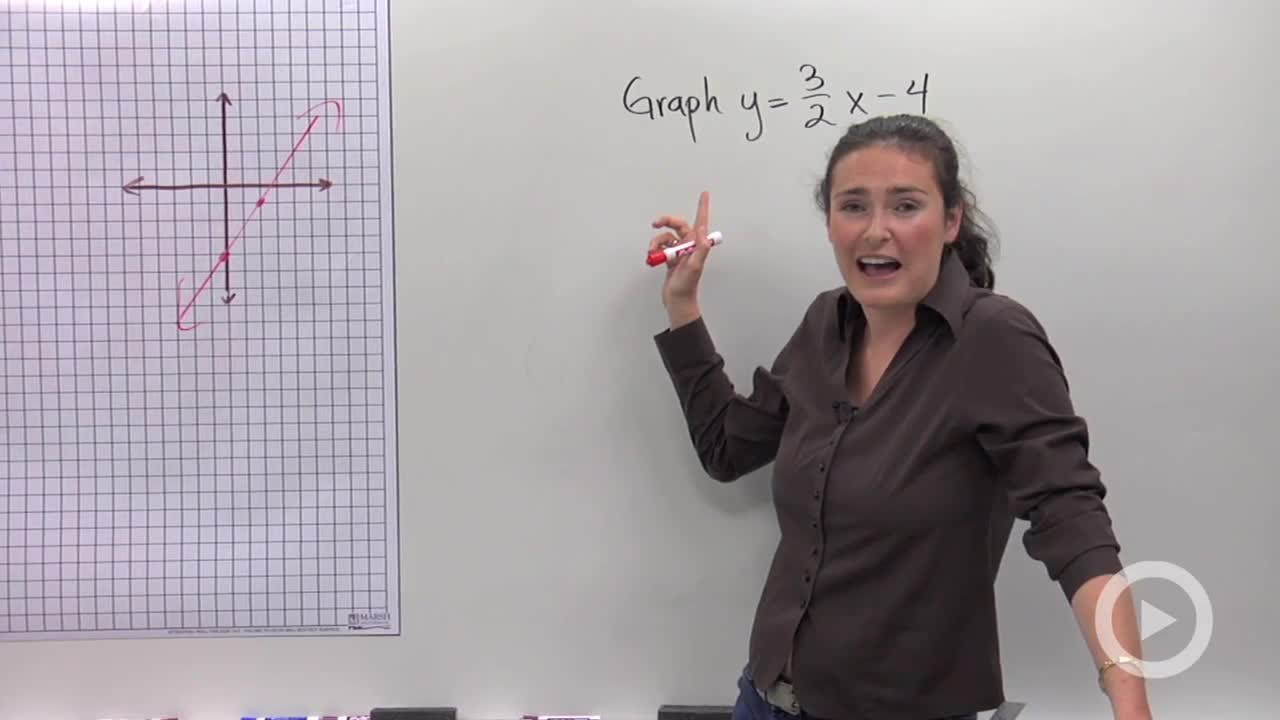
How To Graph A Line Using Y Mx B Problem 1 Algebra Video By Brightstorm
Slope Intercept Form Calculator
Linear Equations Objectives Find Slope Of A Line Ppt Download

Standard 4 To Ma Conversion Formula Instrumentationtools
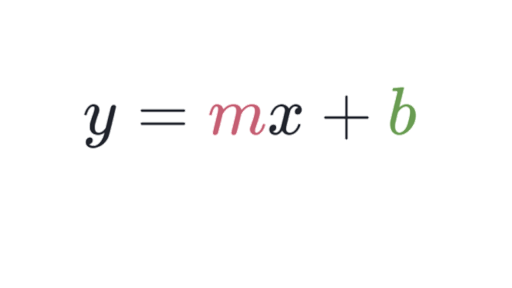
Slope Intercept Form Introduction Algebra Article Khan Academy
Q Tbn And9gcqoydrypjrzdpxsiatbq4txzrr8osfsot9un4o3 Sx4zrowjpca Usqp Cau
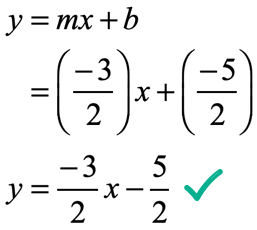
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath
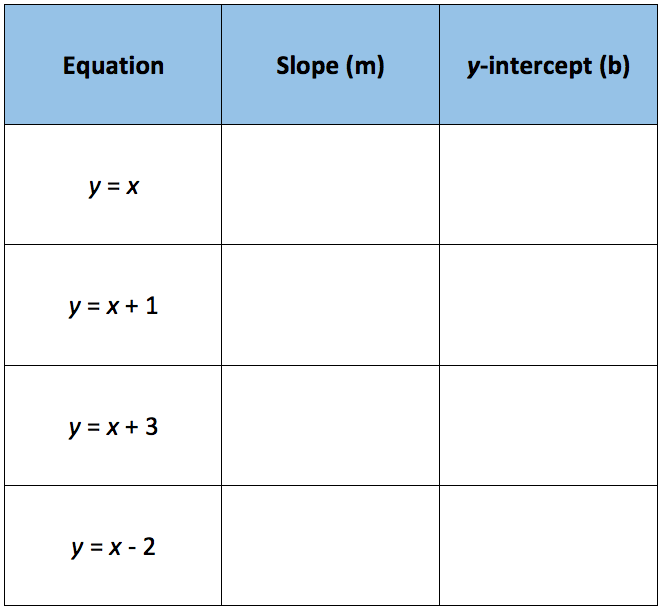
Analyzing The Effects Of The Changes In M And B On The Graph Of Y Mx B Texas Gateway

Ex 10 3 1 Reduce Equations Into Slope Intercept Form Ex 10 3
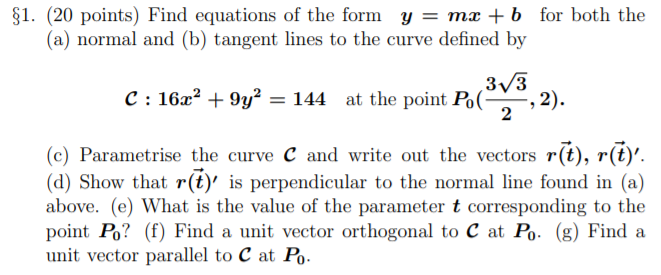
Solved 1 Points Find Equations Of The Form Y Mx Chegg Com
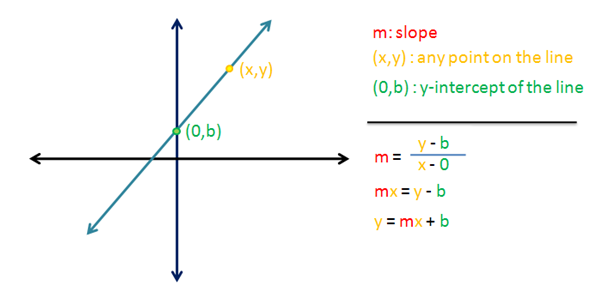
Equation Of A Line The Derivation Of Y Mx B
Solved Slope Of A Graph And Linear Inequalities Solve The Following Exercises Step By Step Using Formulas The Lopez Company Is Dedicated To The Ma Course Hero
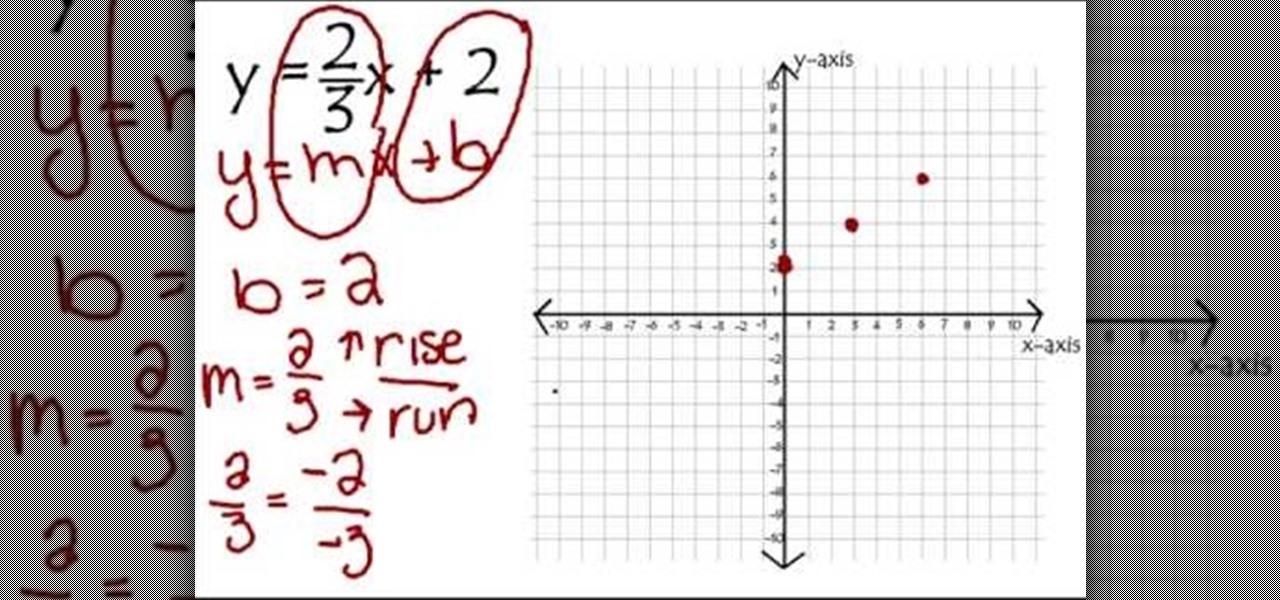
How To Graph Linear Equations Using Y Mx B Math Wonderhowto

6 2 Graphing Linear Equations

Graph A Linear Equation Graph 2x 3y 12 Solve For Y So The Equation Looks Like Y Mx B 3y 2x 12 Subtract 2x To Both Sides Y X 4 Divide Ppt Download
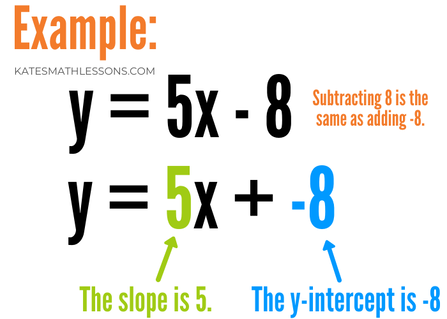
Writing Linear Equations Using The Slope Intercept Form Algebra 1 Formulating Linear Equations Mathplanet
2

Solve For X And Y Mx Ny M 2 N 2 And X Y 2m
1

Solve The Formula Y Mx B For M Brainly Com

Graphical Analysis Of One Dimensional Motion Physics

Gmat Math Lines Slope In The X Y Plane Magoosh Blog Gmat Exam
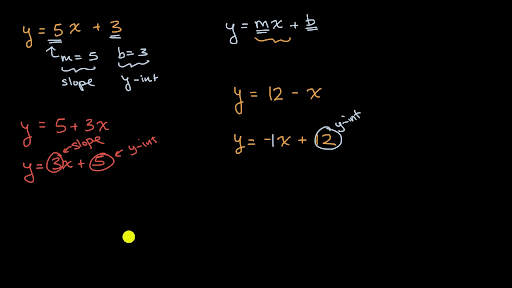
Slope And Y Intercept From Equation Video Khan Academy
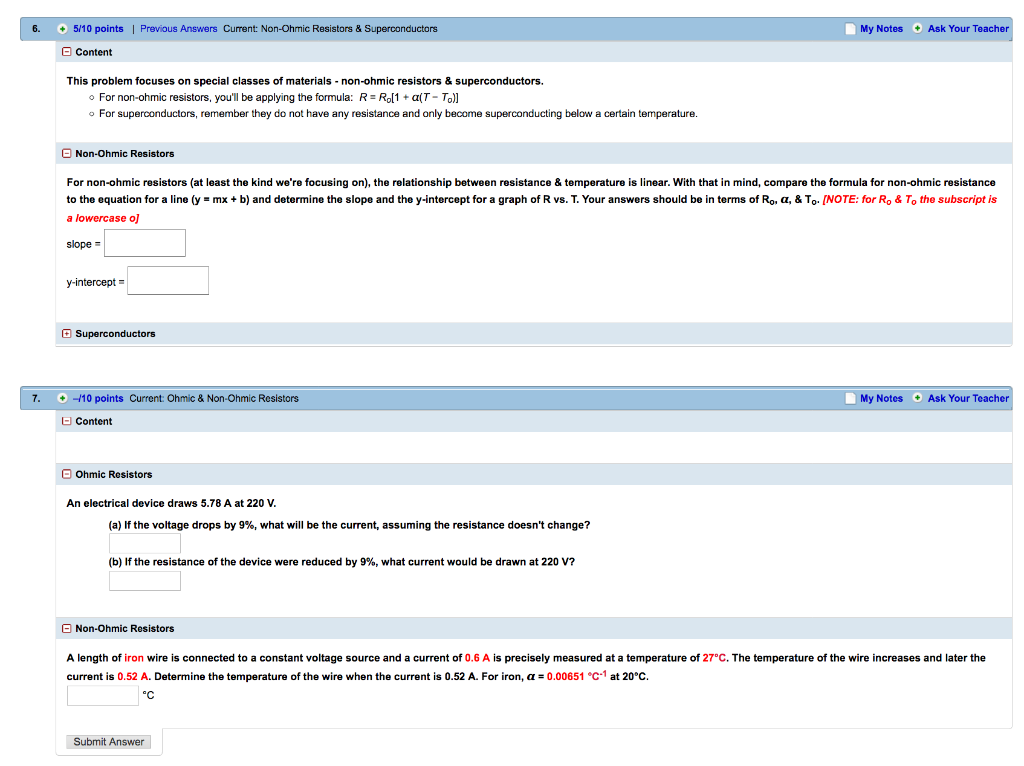
Solved For Non Ohmic Resistors At Least The Kind We Re F Chegg Com

Solve 2x 3y 11 And 2x 4y 24 And Hence Find The Value Of M For Which Y Mx 3

Use The Slope Intercept Form Of An Equation Of A Line Elementary Algebra

Update Picture Here A Write The Equations Of The Lines In Slope Intercept Form Y Mx B You Should Brainly In

Nts

3 Ways To Find The Y Intercept Wikihow
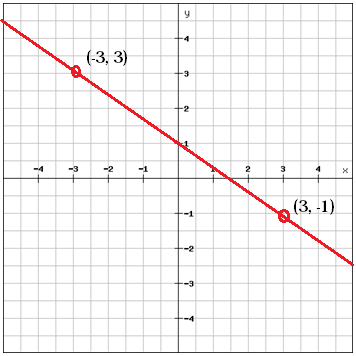
Using Two Points To Write An Equation In Slope Intercept Form Kate S Math Lessons

Determining Activation Energy
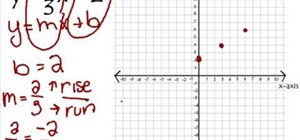
How To Graph Linear Equations Using Y Mx B Math Wonderhowto
Y Mx C High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Slope Of The Graph Of Y Mx C What Is The Graph Of Y Mx C
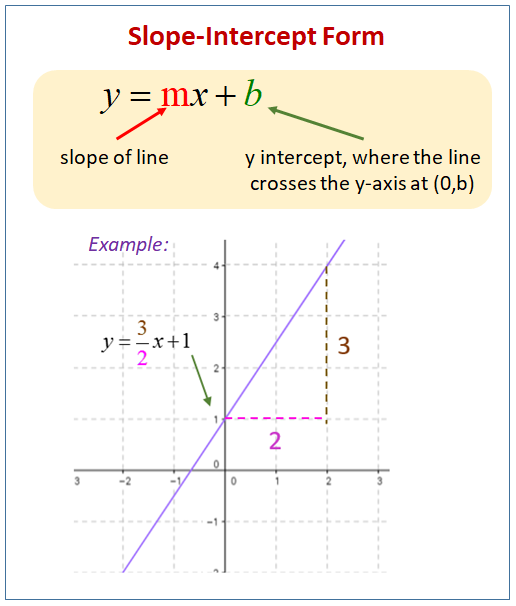
Equation Of Line Solutions Examples Videos
Straight Line Equations Slope Intercept Form Purplemath

Standard 4 To Ma Conversion Formula Instrumentationtools

Y Mx C Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme
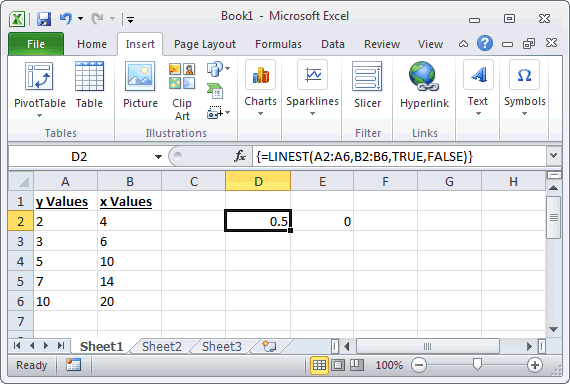
Ms Excel How To Use The Linest Function Ws
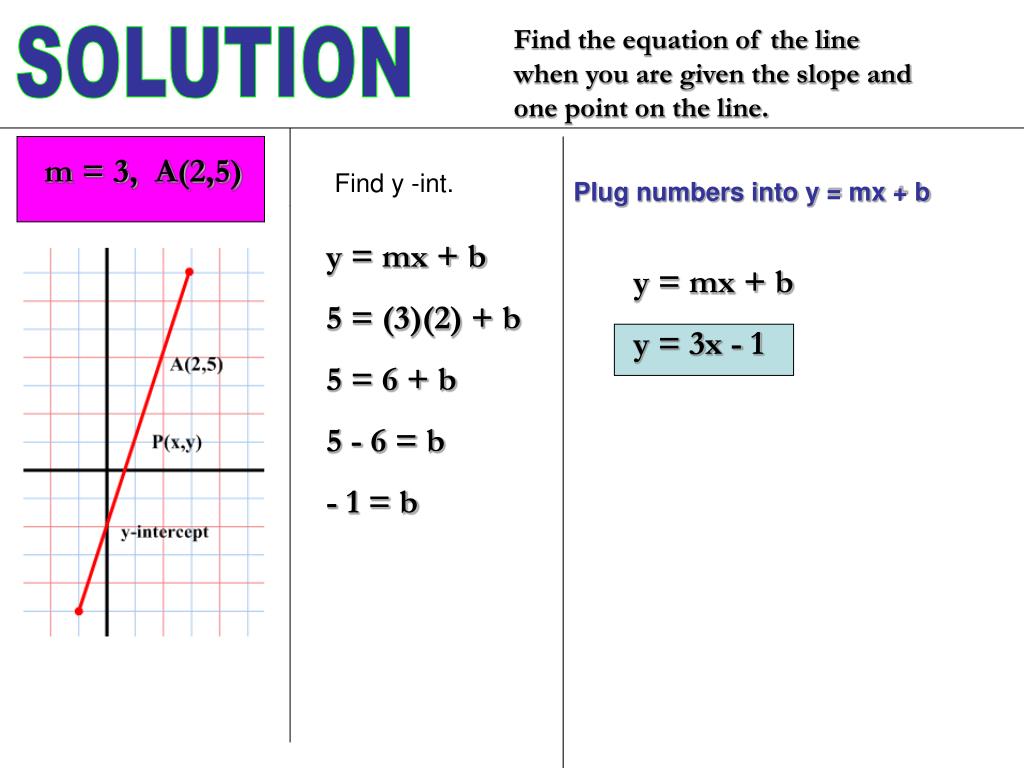
Ppt Y Mx B Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
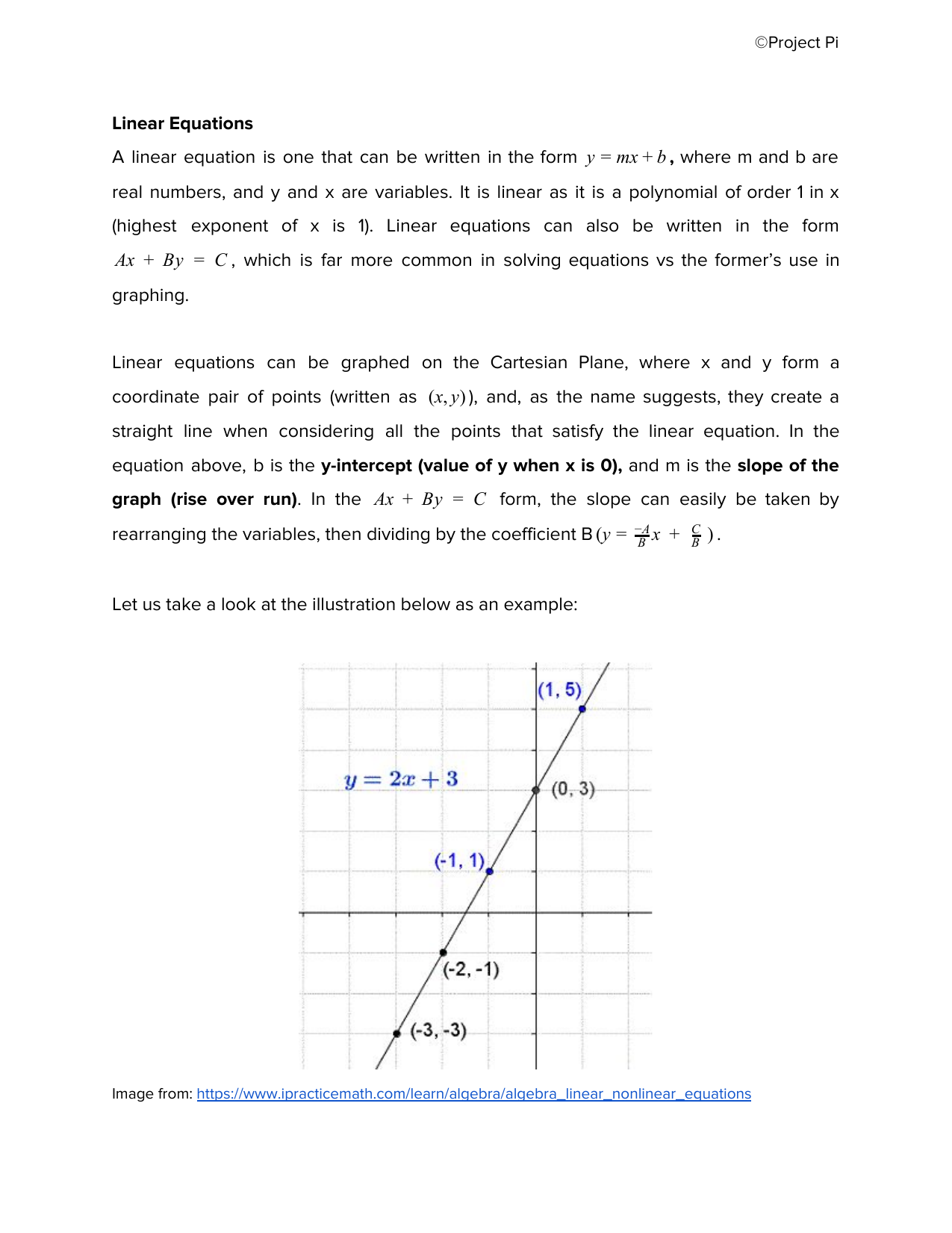
Algebra Linear Equations And Inequalities Notes
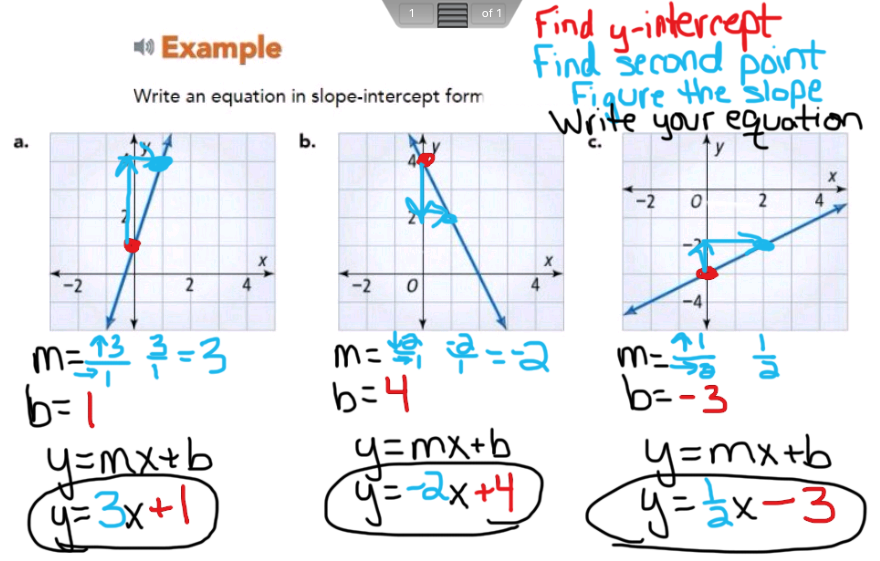
Graphing In Y Mx B Format Rlas 8th Grade Math

Edexcel Core Mathematics C1 May 17 Worksheets Videos Examples Solutions Activities

Misc 21 Line Y Mx 1 Is Tangent To Y2 4x If Value Of M Is

What Is Y Mx C Quora

Ex 10 3 15 Perpendicular From The Origin To Y Mx C
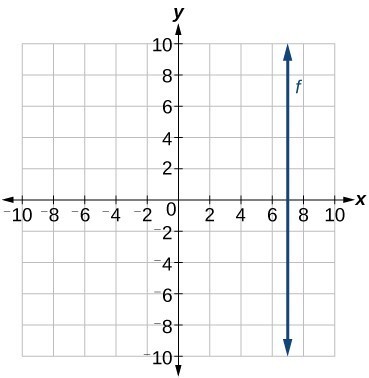
Write The Equation For A Linear Function From The Graph Of A Line College Algebra

Gradient Slope Intercept Form Passy S World Of Mathematics

3 Ways To Find The Y Intercept Wikihow
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/LinearRelationshipDefinition2-a62b18ef1633418da1127aa7608b87a2.png)
Linear Relationship Definition
Y Mx C Equation Of A Line Youtube
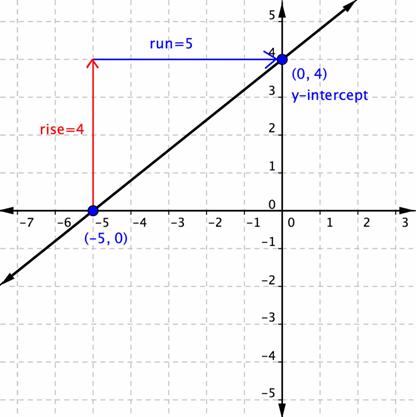
Writing The Equation Of A Line
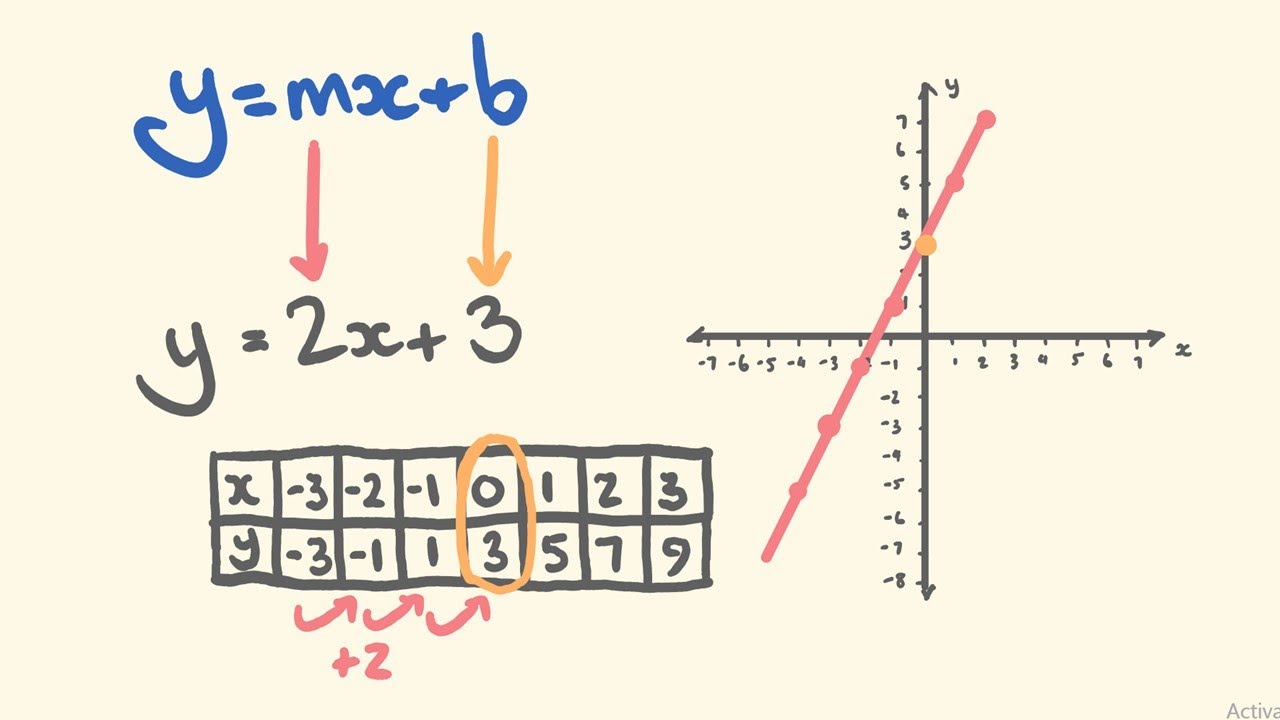
Graphing Linear Equations Using Y Mx B Slope Intercept Youtube
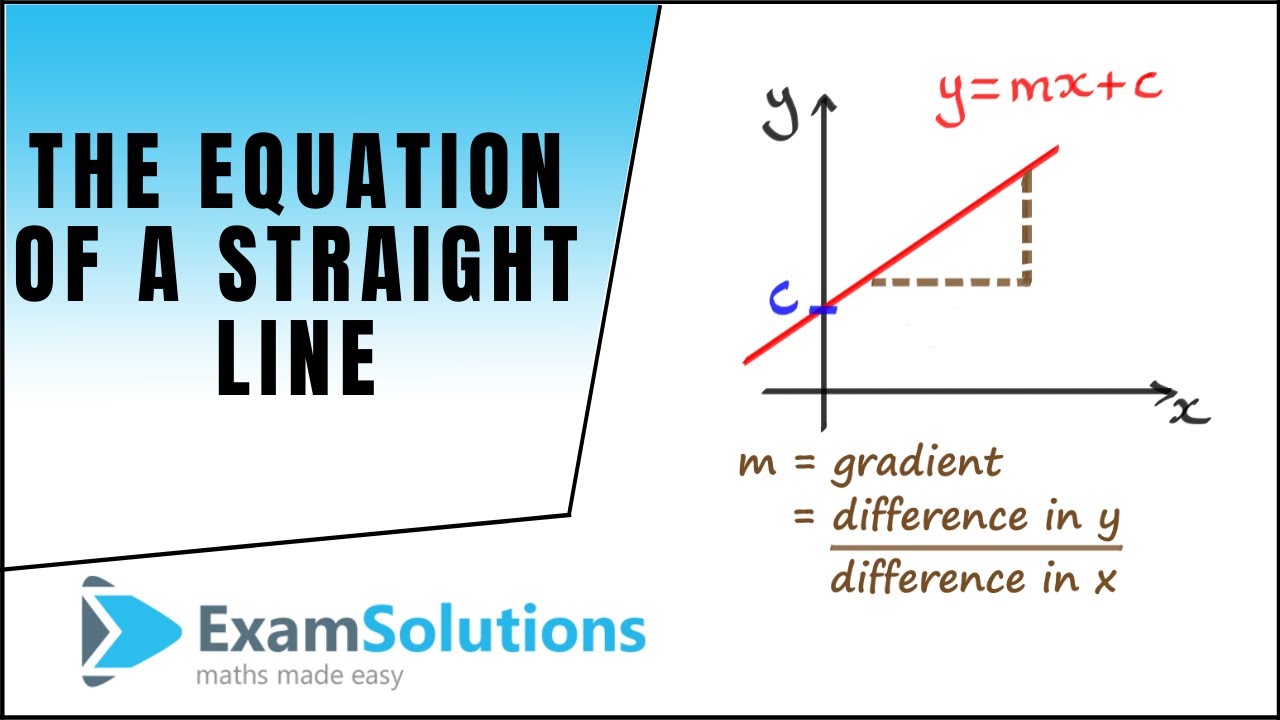
How To Find The Equation Of A Straight Line Y Mx C Youtube
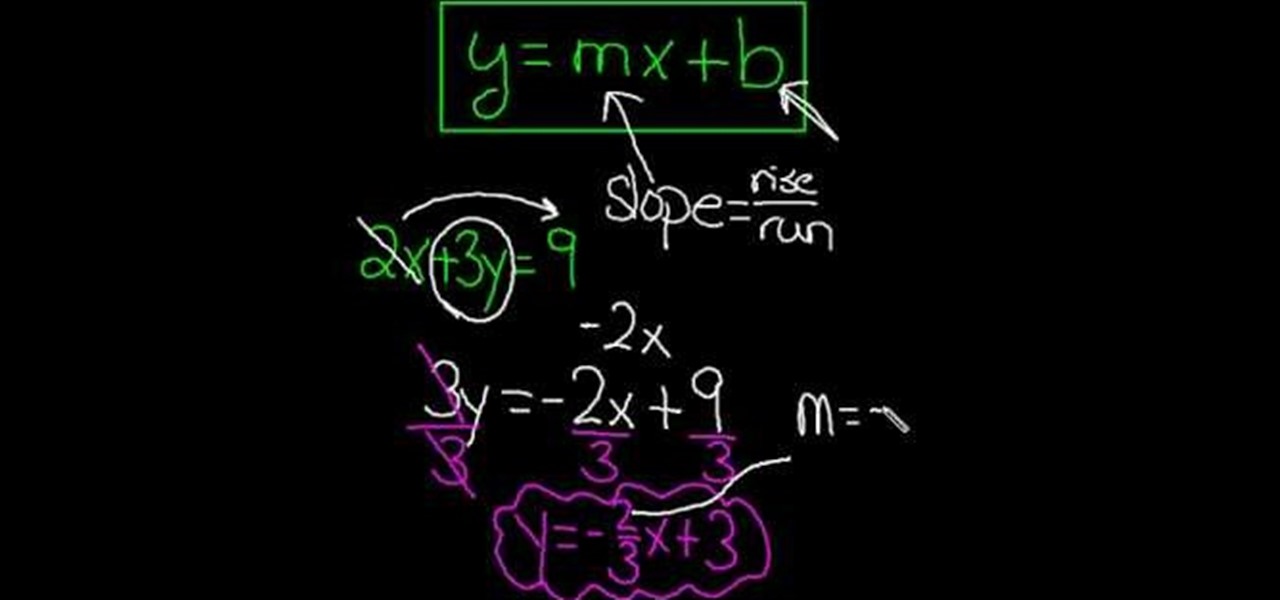
How To Solve Algebraic Equations With The Y Mx B Format Math Wonderhowto

Graphing Parabolas



